Heat-inactivated Lacticaseibacillus paracasei N1115 alleviates the damage due to brain function caused by long-term antibiotic cocktail exposure in mice
- PMID: 35754018
- PMCID: PMC9233843
- DOI: 10.1186/s12868-022-00724-w
Heat-inactivated Lacticaseibacillus paracasei N1115 alleviates the damage due to brain function caused by long-term antibiotic cocktail exposure in mice
Abstract
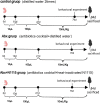
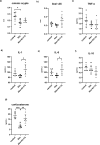
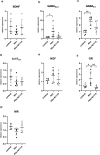
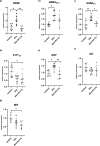
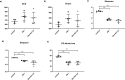
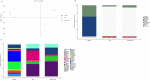
Critical development period of intestinal microbiota occurs concurrently with brain development, and their interaction is influenced by the microbiota-gut-brain axis. This study examined how antibiotics exposure affected gut microbiota and brain development and analyzed the possible benefits of heat-inactivated Lacticaseibacillus paracasei N1115 (N1115). Thirty neonatal male mice were randomly divided into three groups and treated with sterilized water (control), an antibiotic cocktail (Abx), or antibiotics plus heat-inactivated N1115 (Abx + N1115) for 84 days. We found that while the mRNA levels of GABAAα1, GABAb1, and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) in the hippocampus and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), GABAAα1, GABAb1, and nerve growth factor (NGF) in the prefrontal cortex were higher, the mRNA levels of 5-HT1A were lower in the Abx group. The Abx + N1115 group had lower mRNA levels of GABAAα1, GABAb1, and GR in the hippocampus and BDNF, GABAb1, and NGF in the prefrontal cortex than the Abx group. The latency period was longer in the Morris water maze test while longer rest time was seen in tail suspension test in the Abx group than the control and Abx + N1115 groups. In the open field test, the moving time and distance of the Abx group were reduced. Further, the alpha-diversity indexes of the Abx and Abx + N1115 groups were significantly lower than the control. Further, long-term exposure to antibiotics disrupted the intestinal microbiota as evidenced by decreased Bacteroides, Firmicutes, and Lactobacillus, and increased Proteobacteria and Citrobacter. However, N1115 significantly decreased the abundance of Citrobacter when compared with those in the Abx group. These results indicate that antibiotics can substantially damage the intestinal microbiota and cognitive function, causing anxiety and depression, which can be alleviated by heat-inactivated N1115 via modulation of the microbiota-gut-brain axis.
Keywords: Antibiotic; Cognitive function; Microbiota–gut–brain axis; Paraprobiotic.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

