Scale-attentional U-Net for the segmentation of the median nerve in ultrasound images
- PMID: 35754116
- PMCID: PMC9532202
- DOI: 10.14366/usg.21214
Scale-attentional U-Net for the segmentation of the median nerve in ultrasound images
Abstract
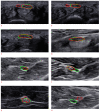
Purpose: The aim of this study was to develop a neural network that accurately and effectively segments the median nerve in ultrasound (US) images.
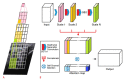
Methods: In total, 1,305 images of the median nerve of 123 normal subjects were used to train and evaluate the model. Four datasets from two measurement regions (wrist and forearm) of the nerve and two US machines were used. The neural network was designed for high accuracy by combining information at multiple scales, as well as for high efficiency to prevent overfitting. The model was designed in two parts (cascaded and factorized convolutions), followed by selfattention over scale and channel features. The precision, recall, dice similarity coefficient (DSC), and Hausdorff distance (HD) were used as performance metrics. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was also assessed.
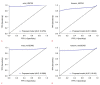
Results: In the wrist datasets, the proposed network achieved 92.7% and 90.3% precision, 92.4% and 89.8% recall, DSCs of 92.3% and 89.7%, HDs of 5.158 and 4.966, and AUCs of 0.9755 and 0.9399 on two machines. In the forearm datasets, 79.3% and 87.8% precision, 76.0% and 85.0% recall, DSCs of 76.1% and 85.8%, HDs of 5.206 and 4.527, and AUCs of 0.8846 and 0.9150 were achieved. In all datasets, the model developed herein achieved better performance in terms of DSC than previous U-Net-based systems.
Conclusion: The proposed neural network yields accurate segmentation results to assist clinicians in identifying the median nerve.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Median nerve; Neural networks; Ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automatic prostate segmentation using deep learning on clinically diverse 3D transrectal ultrasound images.Med Phys. 2020 Jun;47(6):2413-2426. doi: 10.1002/mp.14134. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32166768
-
A multiple-channel and atrous convolution network for ultrasound image segmentation.Med Phys. 2020 Dec;47(12):6270-6285. doi: 10.1002/mp.14512. Epub 2020 Oct 18. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 33007105
-
Attention-VGG16-UNet: a novel deep learning approach for automatic segmentation of the median nerve in ultrasound images.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022 Jun;12(6):3138-3150. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-1074. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022. PMID: 35655843 Free PMC article.
-
A two-stage network with prior knowledge guidance for medullary thyroid carcinoma recognition in ultrasound images.Med Phys. 2022 Apr;49(4):2413-2426. doi: 10.1002/mp.15492. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 35103313
-
Transformer-Based Automated Segmentation of the Median Nerve in Ultrasound Videos of Wrist-to-Elbow Region.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2024 Jan;71(1):56-69. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2023.3330539. Epub 2024 Jan 9. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2024. PMID: 37930930
Cited by
-
Investigation of Appropriate Scaling of Networks and Images for Convolutional Neural Network-Based Nerve Detection in Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Blocks.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jun 6;24(11):3696. doi: 10.3390/s24113696. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38894486 Free PMC article.
-
From Visualization to Automation: A Narrative Review of Deep Learning's Impact on Ultrasound-based Median Nerve Assessment.J Med Ultrasound. 2025 May 23;33(2):95-101. doi: 10.4103/jmu.JMU-D-25-00010. eCollection 2025 Apr-Jun. J Med Ultrasound. 2025. PMID: 40521317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Supported Ultrasonography in Anesthesiology: Evaluation of a Patient in the Operating Theatre.J Pers Med. 2024 Mar 15;14(3):310. doi: 10.3390/jpm14030310. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38541052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep-learning segmentation of fascicles from microCT of the human vagus nerve.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 10;17:1169187. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1169187. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37332862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walker FO, Cartwright MS, Alter KE, Visser LH, Hobson-Webb LD, Padua L, et al. Indications for neuromuscular ultrasound: expert opinion and review of the literature. Clin Neurophysiol. 2018;129:2658–2679. - PubMed
-
- Cartwright MS, Hobson-Webb LD, Boon AJ, Alter KE, Hunt CH, Flores VH, et al. Evidence-based guideline: neuromuscular ultrasound for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2012;46:287–293. - PubMed
-
- Kim SC, Hauser S, Staniek A, Weber S. Learning curve of medical students in ultrasound-guided simulated nerve block. J Anesth. 2014;28:76–80. - PubMed
-
- da Silva L, Sellera FP, Gargano RG, Rossetto TC, Gomes GB, Miyahira FT, et al. Preliminary study of a teaching model for ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blockade and effects on the learning curve in veterinary anesthesia residents. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2017;44:684–687. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

