Accelerated dual-venc 4D flow MRI with variable high-venc spatial resolution for neurovascular applications
- PMID: 35754143
- PMCID: PMC9392495
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29306
Accelerated dual-venc 4D flow MRI with variable high-venc spatial resolution for neurovascular applications
Abstract
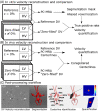
Purpose: Dual-velocity encoded (dual-venc or DV) 4D flow MRI achieves wide velocity dynamic range and velocity-to-noise ratio (VNR), enabling accurate neurovascular flow characterization. To reduce scan time, we present interleaved dual-venc 4D Flow with independently prescribed, prospectively undersampled spatial resolution of the high-venc (HV) acquisition: Variable Spatial Resolution Dual Venc (VSRDV).
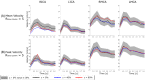
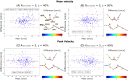
Methods: A prototype VSRDV sequence was developed based on a Cartesian acquisition with eight-point phase encoding, combining PEAK-GRAPPA acceleration with zero-filling in phase and partition directions for HV. The VSRDV approach was optimized by varying z, the zero-filling fraction of HV relative to low-venc, between 0%-80% in vitro (realistic neurovascular model with pulsatile flow) and in vivo (n = 10 volunteers). Antialiasing precision, mean and peak velocity quantification accuracy, and test-retest reproducibility were assessed relative to reference images with equal-resolution HV and low venc (z = 0%).
Results: In vitro results for all z demonstrated an antialiasing true positive rate at least 95% for = 2 and 5, with no linear relationship to z (p = 0.62 and 0.13, respectively). Bland-Altman analysis for z = 20%, 40%, 60%, or 80% versus z = 0% in vitro and in vivo demonstrated no bias >1% of venc in mean or peak velocity values at any . In vitro mean and peak velocity, and in vivo peak velocity, had limits of agreement within 15%.
Conclusion: VSRDV allows up to 34.8% scan time reduction compared to PEAK-GRAPPA accelerated DV 4D Flow MRI, enabling large spatial coverage and dynamic range while maintaining VNR and velocity measurement accuracy.
Keywords: 4D flow; acceleration; acquisition; dual-venc; neurovascular.
© 2022 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Jianing Pang is an employee of Siemens Medical Solutions USA. Dr. Michael Markl receives research support from Siemens and Circle Cardiovascular Imaging.
Figures




References
-
- Schnell S, Ansari SA, Vakil P, et al. Characterization of cerebral aneurysms using 4D FLOW MRI. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2012;14:W2.
-
- Orita E, Murai Y, Sekine T, et al. Four‐dimensional flow MRI analysis of cerebral blood flow before and after high‐flow extracranial–intracranial bypass surgery with internal carotid artery ligation. Neurosurgery. 2018;85:58‐64. - PubMed
-
- Hope TA, Purcell DD, von Morze C, Vigneron DB, Alley MT, Dillon WP. Evaluation of intracranial stenoses and aneurysms with accelerated 4D flow. Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;28(1):41‐46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

