Comparative analysis of loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with microfluidic chip technology and q-PCR in the detection of clinical infectious pathogens
- PMID: 35754145
- PMCID: PMC9396168
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24565
Comparative analysis of loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with microfluidic chip technology and q-PCR in the detection of clinical infectious pathogens
Abstract
Background: Rapid diagnosis of infectious pathogens at an early stage is crucial to stabilize the patient's condition, reduce medical costs, and shorten hospital stays. Currently, some point-of-care tests have their own shortcomings. Therefore, we built a microfluidic chip based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification to can quickly and sensitively detect infectious pathogens.
Methods: We extracted the DNA of S. aureus, MRSA, Shigella and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Then, the DNA samples were diluted by 10-fold and examined by two methods: LAMP-microfluidic chip and q-PCR, the sensitivity of whom was also compared. In addition, the specificity of the two was also examined by detecting the target bacteria and other microorganisms using the same methods. Finally, we extracted and tested the DNA of clinically infected humoral samples to determine the coincidence rate between the two methods and the bacterial culture method.
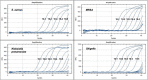
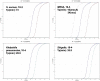
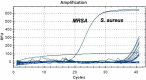
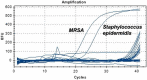
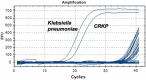
Results: For S. aureus, MRSA, Shigella, and Klebsiella pneumoniae, the detection limits of the chip were 2.25 × 103 copies/μl, 5.32 × 103 copies/μl, 2.89 × 103 copies/μl, 6.53 × 102 copies/μl, and the detection limits of q-PCR were 2.25 × 102 copies/μl, 5.32 × 101 copies/μl, 2.89 × 102 copies/μl, 6.53 × 101 copies/μl, respectively. In terms of detection specificity, neither method cross-reacted with other strains. For the detection of infectious humoral samples, the total coincidence rate between the q-PCR and bacterial culture method was 85.7%, 95%, 95%, and 95.5%, and the total coincidence rate between the chip and bacterial culture method was 81%, 95%, 90%, and 86.4%, respectively.
Conclusion: LAMP-microfluidic chip provides a simple, sensitive, specific, convenient, and rapid pathogen detection method for clinically infected humoral samples without relying on expensive equipment or technical personnels.
Keywords: bacteria; chip; detection; loop-mediated isothermal amplification; microfluidics.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the ICMJE Form for Potential Conflicts of Interest and have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

