Dual effect of radiotherapy related concomitant cardiovascular diseases in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35754191
- PMCID: PMC9883436
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.4948
Dual effect of radiotherapy related concomitant cardiovascular diseases in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Nowadays, cancer and cardiac diseases are two of the most causes of death, so cancer treatment-related cardiac death cannot be ignored. For lung cancer, chest radiotherapy (RT) is essential, but the related cardiotoxicity has not been fully studied.
Methods: We reviewed the data of 11,455 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database from 2001 to 2015. The change trend for concomitant cardiovascular diseases (CVD)-specific death was calculated and graphically demonstrated. Univariate and multivariate analyses for survival were performed using Cox risk regression model.
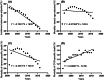
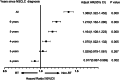
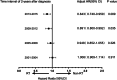
Results: In our analysis, the overall incidence and mortality from NSCLC declined, but CVD-specific death increased. Both chemoradiotherapy and radiotherapy alone played a significant role in CVD-specific death. Analyzed longitudinally from diagnosis, we found that the effect of RT in CVD-specific death increased continuously over the third years and the hazard ratio for CVD-specific death was 1.386 times between RT and non-RT group (HR = 1.386, 95% CI 1.322-1.452; p < 0.0001). On the other hand, RT played a protective role in CVD-specific death before the second years, especially in recent years from 2013 to 2015 (HR = 0.843, 95% CI 0.740-0.959; p = 0.009).
Conclusions: Although the mortality from NSCLC decreased, but radiotherapy-related CVD-specific mortality cannot be ignored. In the long-term over 3 years, RT significantly promoted CVD-specific death. However, RT turned to be a protective role in the short-term within 2 years. In clinical practice, we need to comprehensively consider the dual effects of radiotherapy on the side effect of heart.
Keywords: cardiac deaths; epidemiology; mortality; non-small cell lung cancer; radiation therapy.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular disease-specific mortality in 270,618 patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Cardiol. 2021 May 1;330:186-193. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.02.025. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Int J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33581175
-
Cardiac Radiation Dose, Cardiac Disease, and Mortality in Patients With Lung Cancer.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Jun 18;73(23):2976-2987. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.500. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31196455
-
Dosimetric Predictors of Cardiotoxicity in Thoracic Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;20(6):435-441. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2019.05.014. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Clin Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31303452
-
Safety and Efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with radiotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2021 Feb;10(4):1222-1239. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3718. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33465302 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: preclinical and early clinical data.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004 Feb;18(1):41-53. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8588(03)00138-2. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004. PMID: 15005280 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac Arrhythmias in Patients Treated for Lung Cancer: A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 6;15(24):5723. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245723. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136269 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . World Cancer Report: Cancer Research for Cancer Prevention. (2020). [Accessed November 16, 2020]. https://publicationsiarcfr/586 2020.
-
- Sun JY, Zhang ZY, Qu Q, et al. Cardiovascular disease‐specific mortality in 270,618 patients with non‐small cell lung cancer. Int J Cardiol. 2021;330:186‐193. - PubMed
-
- Ladbury CJ, Rusthoven CG, Camidge DR, Kavanagh BD, Nath SK. Impact of radiation dose to the host immune system on tumor control and survival for stage III non‐small cell lung cancer treated with definitive radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;105:346‐355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

