Umbilical Artery Systolic/Diastolic Ratio and Amniotic Fluid Index in Prediction of Adverse Perinatal Outcome in Term Pregnancies
- PMID: 35754662
- PMCID: PMC9215189
- DOI: 10.4103/ijabmr.ijabmr_452_21
Umbilical Artery Systolic/Diastolic Ratio and Amniotic Fluid Index in Prediction of Adverse Perinatal Outcome in Term Pregnancies
Abstract
Background: Antenatal fetal surveillance is a field of increasing importance in modern obstetrics. It is based on fetal heart rate monitoring using nonstress test and contraction stress test, ultrasound biometry and amniotic fluid assessment, Doppler blood flow studies of fetal and uteroplacental circulation, and an evaluation of biophysical fetal parameters. The combination of these methods leads to improvements in fetal morbidity and mortality.
Aim: The present study aimed to assess the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of umbilical artery (UA) systolic/diastolic (S/D) ratio, and amniotic fluid index (AFI) in term pregnancies for the prediction of perinatal outcome and their relation with perinatal outcome.
Methods: This study was conducted at a tertiary care hospital on 100 pregnant women where all the term singleton pregnancies (37-42 weeks) admitted in maternity were subjected to color Doppler for UA S/D ratio assessment and AFI estimation. Further, management of patients was done according to color Doppler findings and their relation with perinatal outcome.
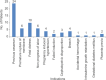
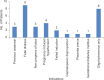
Results: Out of 100 pregnant women, 68% had AFI >8 (normal), while 32% of women had AFI <8 (abnormal), with the mean AFI being 9.39 ± 2.55 cm, whereas70% had S/D ratio <3 (normal) and 30% of women had S/D ratio >3 (abnormal), with the mean S/D ratio of 2.61 ± 0.450. UA S/D ratio had better performance values (i.e., sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive value) than AFI in predicting adverse perinatal outcomes.
Conclusion: AFI and UA S/D ratio are important for predicting low appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration score, meconium, respiratory complications, and perinatal mortality in high as well as low-risk pregnancy cases. However, UA S/D ratio is a better predictor of perinatal outcome in high-risk pregnancies.
Keywords: Amniotic fluid index; activity; and respiration; appearance; color doppler; grimace; meconium; negative predictive value; perinatal outcome; positive predictive value; pulse; sensitivity; specificity; umbilical artery systolic/diastolic ratio.
Copyright: © 2022 International Journal of Applied and Basic Medical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abnormal Doppler velocimetry is related to adverse perinatal outcome for borderline amniotic fluid index during third trimester.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2006 Dec;32(6):545-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.2006.00459.x. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2006. PMID: 17100815
-
Predictive value of doppler cerebroplacental ratio for adverse perinatal outcomes in postdate pregnancies in Northwestern Nigeria.Niger J Clin Pract. 2022 Apr;25(4):406-414. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_14_21. Niger J Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 35439898
-
Middle cerebral to umbilical artery Doppler ratio in post-date pregnancies.Obstet Gynecol. 1994 Nov;84(5):856-60. Obstet Gynecol. 1994. PMID: 7936526
-
[Management of post-term pregnancies: the role for AFI, biophysical score and doppler].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2011 Dec;40(8):785-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2011.09.020. Epub 2011 Nov 9. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2011. PMID: 22078136 Review. French.
-
Comparison between cerebroplacental ratio and umbilicocerebral ratio in predicting adverse perinatal outcome at term.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020 Sep;252:439-443. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.07.032. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020. PMID: 32763648 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Perinatal Outcomes in Pregnant Women With Low Amniotic Fluid Index.J Family Reprod Health. 2023 Dec;17(4):199-204. doi: 10.18502/jfrh.v17i4.14591. J Family Reprod Health. 2023. PMID: 38807617 Free PMC article.
-
Antenatal diagnosis of bronchopulmonary sequestration: A case report and review of the literature.Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Nov 24;19(2):604-613. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.10.061. eCollection 2024 Feb. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 38111561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goyal S, Suresh A, Rao AA. Amniotic fluid index versus umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry in prediction of perinatal outcome. Int J Innov Res Dev. 2014;3:91–4.
-
- Arduini D, Rizzo G, Romanini C. Changes of pulsatility index from fetal vessels preceding the onset of late decelerations in growth-retarded fetuses. Obstet Gynecol. 1992;79:605–10. - PubMed
-
- Sterne G, Shields LE, Dubinsky TJ. Abnormal fetal cerebral and umbilical Doppler measurements in fetuses with intrauterine growth restriction predicts the severity of perinatal morbidity. J Clin Ultrasound. 2001;29:146–51. - PubMed
-
- Arias F. Accuracy of the middle-cerebral-to-umbilical-artery resistance index ratio in the prediction of neonatal outcome in patients at high risk for fetal and neonatal complications. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;171:1541–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources