Efficacy of Modified Qingre Jiedu Decoction Combined with Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy in Treating Moderate to Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma and Its Effect on Levels of Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen and Carbohydrate Antigen 125
- PMID: 35754698
- PMCID: PMC9217599
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1821719
Efficacy of Modified Qingre Jiedu Decoction Combined with Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy in Treating Moderate to Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma and Its Effect on Levels of Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen and Carbohydrate Antigen 125
Abstract
Objective: To explore the efficacy of modified Qingre Jiedu decoction combined with three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) in treating moderate to advanced ovarian carcinoma (OC) and its effect on patients' serum carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA125).
Methods: The clinical data of 84 patients with moderate to advanced OC treated in the gynecology department of Changqing District People's Hospital of Jinan from February 2017 to February 2018 were selected for retrospective analysis, and the patients were divided into the single chemotherapy group (taxol + carboplatin, n = 42) and the combined group (modified Qingre Jiedu decoction+3D-CRT, n = 42) according to the parity of their admission numbers. By measuring their levels of serum CEA and CA125 after treatment, the cellular immune levels of the two groups were compared.
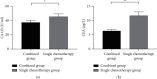
Results: Compared with the single chemotherapy group after treatment, the combined group obtained significantly higher total clinical effective rate and 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year survival rates (P < 0.05), significantly higher CD4+/CD8+ and NK cell level values (P < 0.001), significantly lower serum CA125 and CEA level values (P < 0.001), and significantly lower total incidence rates of toxic and side effects (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The abovementioned results show that the combined treatment modality has a significant effect on prolonging the survival of patients with moderate to advanced OC and can effectively reduce the levels of tumor markers and improve the body's immunity. Further study will be conducive to establishing a better solution for OC patients.
Copyright © 2022 Shufen Ai and Jin Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nilsu Ç., Cenk U., Okan Ö. Dosimetric comparison of anterior posterior-posterior anterior 2-field three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, 4-field three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and “forward” plan intensity modulated radiotherapy techniques in female lymphoma patients irradiated to neck and mediastinum. Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics . 2018;14:1389–1396. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

