Structure and surface analyses of a newly synthesized acyl thiourea derivative along with its in silico and in vitro investigations for RNR, DNA binding, urease inhibition and radical scavenging activities
- PMID: 35755589
- PMCID: PMC9185314
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra03160d
Structure and surface analyses of a newly synthesized acyl thiourea derivative along with its in silico and in vitro investigations for RNR, DNA binding, urease inhibition and radical scavenging activities
Abstract
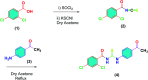
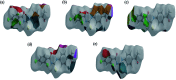
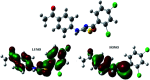
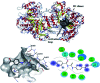
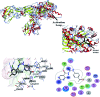
N-((4-Acetylphenyl)carbamothioyl)-2,4-dichlorobenzamide (4) was synthesized by the treatment of 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl chloride with potassium thiocyanate in a 1 : 1 molar ratio in dry acetone to afford the 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl isothiocyanate in situ which on reaction with acetyl aniline furnished (4) in good yield and high purity. The compound was confirmed by FTIR, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR and single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. The planar rings were situated at a dihedral angle of 33.32(6)°. The molecules, forming S(6) ring motifs with the intramolecular N-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, were linked through intermolecular C-H⋯O and N-H⋯S hydrogen bonds, enclosing R2 2(8) ring motifs, into infinite double chains along [101]. C-H⋯π and π⋯π interactions with an inter-centroid distance of 3.694 (1) Å helped to consolidate a three-dimensional architecture. Hirshfeld surface (HS) analysis further indicated that the most important contributions for the crystal packing were from H⋯C/C⋯H (20.9%), H⋯H (20.5%), H⋯Cl/Cl⋯H (19.4%), H⋯O/O⋯H (13.8%) and H⋯S/S⋯H (8.9%) interactions. Thus C-H⋯π (ring), π⋯π, van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonding played the major roles in the crystal packing. The electronic structure and computed DFT (density functional theory) parameters identified the reactivity profile of compound (4). In silico binding of (4) with RNA indicated the formation of a stable protein-ligand complex via hydrogen bonding, while DNA docking studies inferred (4) as a potent groove binder. The experimentally observed hypochromic change (57.2%) in the UV-visible spectrum of (4) in the presence of varying DNA concentrations together with the evaluated binding parameters (K b; 7.9 × 104 M-1, ΔG; -28.42 kJ mol-1) indicated spontaneous interaction of (4) with DNA via groove binding and hence supported the findings obtained through docking analysis. This compound also showed excellent urease inhibition activity in both in silico and vitro studies with an IC50 value of 0.0389 ± 0.0017 μM. However, the radical scavenging efficiency of (4) was found to be modest in comparison to vitamin C.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



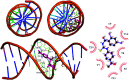


References
-
- Ghorab M. El-Gaby M. S Alsaid M. Elshaier Y. M Soliman A. El-Senduny F. F. A Badria F. Sherif A. Y. A. Novel thiourea derivatives bearing sulfonamide moiety as anticancer agents through COX-2 inhibition. Adv. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017;17:1411–1425. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

