On the Diverse Functions of Electrical Synapses
- PMID: 35755782
- PMCID: PMC9219736
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.910015
On the Diverse Functions of Electrical Synapses
Abstract
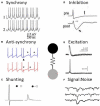
Electrical synapses are the neurophysiological product of gap junctional pores between neurons that allow bidirectional flow of current between neurons. They are expressed throughout the mammalian nervous system, including cortex, hippocampus, thalamus, retina, cerebellum, and inferior olive. Classically, the function of electrical synapses has been associated with synchrony, logically following that continuous conductance provided by gap junctions facilitates the reduction of voltage differences between coupled neurons. Indeed, electrical synapses promote synchrony at many anatomical and frequency ranges across the brain. However, a growing body of literature shows there is greater complexity to the computational function of electrical synapses. The paired membranes that embed electrical synapses act as low-pass filters, and as such, electrical synapses can preferentially transfer spike after hyperpolarizations, effectively providing spike-dependent inhibition. Other functions include driving asynchronous firing, improving signal to noise ratio, aiding in discrimination of dissimilar inputs, or dampening signals by shunting current. The diverse ways by which electrical synapses contribute to neuronal integration merits furthers study. Here we review how functions of electrical synapses vary across circuits and brain regions and depend critically on the context of the neurons and brain circuits involved. Computational modeling of electrical synapses embedded in multi-cellular models and experiments utilizing optical control and measurement of cellular activity will be essential in determining the specific roles performed by electrical synapses in varying contexts.
Keywords: connexin; electrical synapse; gap junction; integration; synchrony.
Copyright © 2022 Vaughn and Haas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

