Understanding the Variation of Bacteria in Response to Summertime Oxygen Depletion in Water Column of Bohai Sea
- PMID: 35756048
- PMCID: PMC9221365
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.890973
Understanding the Variation of Bacteria in Response to Summertime Oxygen Depletion in Water Column of Bohai Sea
Abstract
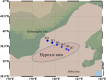
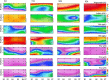
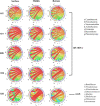
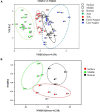
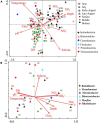
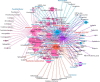
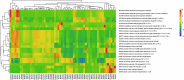
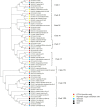
Aiming to reveal the variation in bacteria community under oxygen depletion formed every summer in water column of central Bohai Sea, a time-scenario sampling from June to August in 2018 at a 20-day interval along one inshore-offshore transect was settled. Water samples were collected at the surface, middle, and bottom layer and then analyzed by high-throughput sequencing targeting both 16S rRNA and nosZ genes. Compared to the surface and middle water, oxygen depletion occurred at bottom layer in August. In top two layers, Cyanobacteria dominated the bacterial community, whereas heterotrophic bacteria became dominant in bottom water of Bohai Sea. Based on the time scenario, distinct community separation was observed before (June and July) and after (August) oxygen depletion (p = 0.003). Vertically, strict stratification of nosZ gene was stably formed along 3 sampling layers. As a response to oxygen depletion, the diversity indices of both total bacteria (16S rRNA) and nosZ gene-encoded denitrification bacteria all increased, which indicated the intense potential of nitrogen lose when oxygen depleted. Dissolved oxygen (DO) was the key impacting factor on the community composition of total bacteria in June, whereas nutrients together with DO play the important roles in August for both total and denitrifying bacteria. The biotic impact was revealed further by strong correlations which showed between Cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria in June from co-occurrence network analysis, which became weak in August when DO was depleted. This study discovered the variation in bacteria community in oxygen-depleted water with further effort to understand the potential role of denitrifying bacteria under oxygen depletion in Bohai Sea for the first time, which provided insights into the microbial response to the world-wide expanding oxygen depletion and their contributions in the ocean nitrogen cycling.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; Bohai Sea; bacteria; community variation; nosZ gene; oxygen depletion.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Guo, Li, Song and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aldunate M., De la Iglesia R., Bertagnolli A. D., Ulloa O. (2018). Oxygen modulates bacterial community composition in the coastal upwelling waters off central Chile. Deep Sea Res. 2 Top Stud. Oceanogr. 156 68–79.
-
- Alonso-Gutiérrez J., Figueras A., Albaigés J., Jiménez N., Vinas M., Solanas A. M., et al. (2009). Bacterial communities from shoreline environments (Costa da Morte. Northwestern Spain) affected by the Prestige oil spill. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75 3407–3418. 10.1128/AEM.01776-08 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arevalo-Martínez D. L., Kock A., Schmitz R. A., Bange H. W. (2015). Massive nitrous oxide emissions from the tropical South Pacific Ocean. Nat. Geosci. 8 530–533.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

