The Effect of Examined Lymph Nodes and Lymph Node Ratio on Pathological Nodal Classification in the Lung Adenosquamous Carcinoma After Lobectomy
- PMID: 35756483
- PMCID: PMC9218197
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.909810
The Effect of Examined Lymph Nodes and Lymph Node Ratio on Pathological Nodal Classification in the Lung Adenosquamous Carcinoma After Lobectomy
Abstract
Objective: The effects of examined lymph nodes (LNs) and lymph node ratio (LNR) on pN classification and the prognosis are unclear in lung adenosquamous carcinoma (ASC) patients. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the significance of LNs and LNR in the prognosis of ASC and the impact of the abovementioned factors on the pN classification.
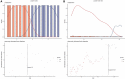
Methods: Patients diagnosed with pathological stage T1-4N0-2M0 ASC from the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results database were included in the study. The primary clinical endpoint was cancer-specific survival (CSS). The optimal cutoff values of the LNs and LNR were determined. An LN indicator, including pN0 #LNs ≤9, pN0 #LNs >9, pN+ #LNR ≤0.53, and pN+ #LNR > 0.53, was developed. Concordance index (C-index) was used to compare the prognostic predictive ability between N classification and LN indicator. The univariable and multivariable Cox regression analyses were used in this study.
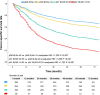
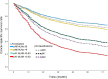
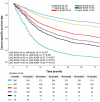
Results: The cohort of 1,416 patients were included in the study. The level of LNs stratified the patients without metastasis of lymph nodes (pN0 #LNs ≤9 vs. pN0 #LNs >9, unadjusted hazard ratio [HR] = 1.255, P = 0.037). Two groups based on the cutoff value of LNR differentiated prognosis of patients with metastasis of lymph nodes (pN+ #LNR >0.53 vs. pN+ #LNR ≤0.53, unadjusted HR = 1.703, P = 0.001). The LN indicator had a much better predictive ability over N classification in this cohort (LN indicator: C-index = 0.615; N classification: C-index = 0.602, P = 0.001).
Conclusions: We explored clinicopathological factors affecting prognosis in resected lung ASC patients. Besides, the LN indicator was confirmed to be played an essential role in affecting the survival rate in ASC patients. The high-level LNs or low-level LNR might be corelated to improved survival outcomes.
Keywords: adenosquamous carcinoma; lymph node; lymph node ratio; non-small cell lung cancer; survival.
Copyright © 2022 Feng, Liu, Huang, Shi and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

