Hepatic Stellate Cell-Immune Interactions in NASH
- PMID: 35757404
- PMCID: PMC9218059
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.867940
Hepatic Stellate Cell-Immune Interactions in NASH
Abstract
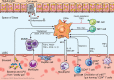
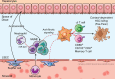
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the dominant cause of liver disease worldwide. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more aggressive presentation of NAFLD, is characterized by severe hepatocellular injury, inflammation, and fibrosis. Chronic inflammation and heightened immune cell activity have emerged as hallmark features of NASH and key drivers of fibrosis through the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Recent advances in our understanding of the molecular and cellular pathways in NASH have highlighted extensive crosstalk between HSCs and hepatic immune populations that strongly influences disease activity. Here, we review these findings, emphasizing the roles of HSCs in liver immunity and inflammation, key cell-cell interactions, and exciting areas for future investigation.
Keywords: NASH; fibrosis; hepatic stellate cells; immunity; inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Carter and Friedman.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, et al. . Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis is the Second Leading Etiology of Liver Disease Among Adults Awaiting Liver Transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology (2015) 148(3):547–55. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.11.039 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

