CAR-T Cell Therapy in Hematological Malignancies: Current Opportunities and Challenges
- PMID: 35757715
- PMCID: PMC9226391
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.927153
CAR-T Cell Therapy in Hematological Malignancies: Current Opportunities and Challenges
Abstract
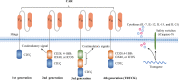
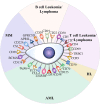
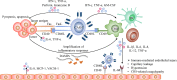
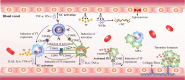
Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy represents a major breakthrough in cancer treatment, and it has achieved unprecedented success in hematological malignancies, especially in relapsed/refractory (R/R) B cell malignancies. At present, CD19 and BCMA are the most common targets in CAR-T cell therapy, and numerous novel therapeutic targets are being explored. However, the adverse events related to CAR-T cell therapy might be serious or even life-threatening, such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS), CAR-T-cell-related encephalopathy syndrome (CRES), infections, cytopenia, and CRS-related coagulopathy. In addition, due to antigen escape, the limited CAR-T cell persistence, and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, a considerable proportion of patients relapse after CAR-T cell therapy. Thus, in this review, we focus on the progress and challenges of CAR-T cell therapy in hematological malignancies, such as attractive therapeutic targets, CAR-T related toxicities, and resistance to CAR-T cell therapy, and provide some practical recommendations.
Keywords: CAR-T cell; CAR-T related toxicities; antigen escape; combinatorial therapy; hematological malignancies; immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Zhu, Zhang, Chen and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Locke FL, Ghobadi A, Jacobson CA, Miklos DB, Lekakis LJ, Oluwole OO, et al. Long-Term Safety and Activity of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 1-2 Trial. Lancet Oncol (2019) 20(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30864-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

