Heparanase Is a Putative Mediator of Endothelial Glycocalyx Damage in COVID-19 - A Proof-of-Concept Study
- PMID: 35757776
- PMCID: PMC9226442
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.916512
Heparanase Is a Putative Mediator of Endothelial Glycocalyx Damage in COVID-19 - A Proof-of-Concept Study
Abstract
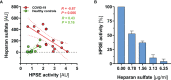
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a systemic disease associated with injury (thinning) of the endothelial glycocalyx (eGC), a protective layer on the vascular endothelium. The aim of this translational study was to investigate the role of the eGC-degrading enzyme heparanase (HPSE), which is known to play a central role in the destruction of the eGC in bacterial sepsis. Excess activity of HPSE in plasma from COVID-19 patients correlated with several markers of eGC damage and perfused boundary region (PBR, an inverse estimate of glycocalyx dimensions of vessels with a diameter 4-25 µm). In a series of translational experiments, we demonstrate that the changes in eGC thickness of cultured cells exposed to COVID-19 serum correlated closely with HPSE activity in concordant plasma samples (R = 0.82, P = 0.003). Inhibition of HPSE by a nonanticoagulant heparin fragment prevented eGC injury in response to COVID-19 serum, as shown by atomic force microscopy and immunofluorescence imaging. Our results suggest that the protective effect of heparin in COVID-19 may be due to an eGC-protective off-target effect.
Keywords: COVID-19; endothelial glycocalyx (EG); heparanase (HPSE); heparin; videomicroscopy.
Copyright © 2022 Drost, Rovas, Osiaevi, Rauen, van der Vlag, Buijsers, Salmenov, Lukasz, Pavenstädt, Linke and Kümpers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

