An Efficient Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis of Cu/Zn Hybrid MOF Nanostructures With High Microbial Strain Performance
- PMID: 35757797
- PMCID: PMC9214199
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.861580
An Efficient Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis of Cu/Zn Hybrid MOF Nanostructures With High Microbial Strain Performance
Retraction in
-
Retraction: An efficient ultrasound-assisted synthesis of Cu/Zn-hybrid MOF nanostructures with high microbial strain performance.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 4;11:1285154. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1285154. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37731765 Free PMC article.
Abstract
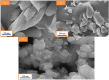
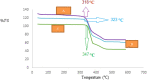
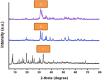
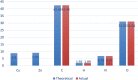
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are a promising choice for antibacterial and antifungal activity due to their composition, unique architecture, and larger surface area. Herein, the ultrasonic method was used to synthesize the Cu/Zn-MOF material as an effective hybrid nanostructure with ideal properties. SEM images were used to investigate the product's morphology and particle size distribution. The XRD pattern revealed that the Cu/Zn hybrid MOF nanostructures had a smaller crystalline size distribution than pure Cu and Zn-MOF samples. Furthermore, the BET technique determined that the hybrid MOF nanostructures had a high specific surface area. TG analysis revealed that the hybrid MOF structures were more thermally stable than pure samples. The final product, with remarkable properties, was used as a new option in the field of antibacterial studies. Antibacterial activity was assessed using MIC and MBC against Gram negative and Gram positive strains, as well as antifungal activity using MIC and MFC. The antimicrobial properties of the synthesized Cu/Zn hybrid MOF nanostructures revealed that they were more effective than commercial drugs in some cases. This study's protocol could be a new strategy for introducing new hybrid nanostructures with specific applications.
Keywords: Cu/Zn MOF; antibacterial nanostructures; antifungal activity; hybrid nanostructures; ultrasound route.
Copyright © 2022 Abdieva, Patra, Al-Qargholi, Shahryari, Chauhan and Moghaddam-manesh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Attri R., Halladj R., Askari S. (2022). Green Route of Flexible Al-MOF Synthesis with Superior Properties at Low Energy Consumption Assisted by Ultrasound Waves. Solid State Sci. 123, 106782. 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2021.106782 - DOI
-
- Al-Rowaili F. N., Jamal A., Ba Shammakh M. S., Rana A. (2018). A Review on Recent Advances for Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol Using Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) and Non-MOF Catalysts: Challenges and Future Prospects. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 15895–15914. 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03843 - DOI
-
- Bah A. R., Kravchuk O., Kirchhof G. (2009). Fitting Performance of Particle-Size Distribution Models on Data Derived by Conventional and Laser Diffraction Techniques. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 73, 1101–1107. 10.2136/sssaj2007.0433 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

