IL-17A deletion reduces sevoflurane-induced neurocognitive impairment in neonatal mice by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 35758051
- PMCID: PMC9342424
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2090608
IL-17A deletion reduces sevoflurane-induced neurocognitive impairment in neonatal mice by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
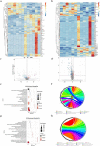
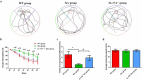
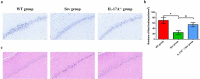
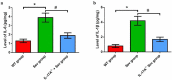
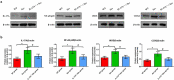
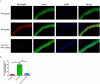
We investigated the role of IL-17A in sevoflurane-inducedneurocognitive impairment in neonatal mice. Seventy-two wild-type (WT) and 42 IL-17A knockout (KO) neonatal mice were randomly divided into WT (n = 36), IL-17A-/- (n = 6), sevoflurane (Sev, n = 36), and IL-17A-/- + sevoflurane (IL-17A-/- + Sev, n = 36) groups. The latter two groups were given 3% sevoflurane for 2 h per day on postnatal days (P) 6-8. Behavioral experiments were performed on P30-36. At P37, RNA sequencing and qRT-PCR of the hippocampus was performed, neurons were detected by Nissl staining, and neuropathological changes were evaluated by HE staining. NF-κB pathway-related proteins were evaluated by western blot and immunofluorescence analyses, IL-1β and IL-6 levels were assessed by ELISA. RNA sequencing identified 131 differentially expressed genes, highlighting several enriched biological processes (chemokine activity, immune response, extracellular region, extracellular space, inflammatory response) and signaling pathways (IL-17 signaling pathway, chemokine signaling pathway, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, ECM-receptor interaction and influenza A). Repeated sevoflurane exposures induced long-term cognitive impairment in WT mice. The cognitive impairment was comparatively less severe in IL-17A KO mice. In addition, the increased levels of NF-κB p65, iNOS, COX-2, IL-17A, IL-6 and IL-1β, reduced neuronal numbers and neuropathological changes were ameliorated in neonatal mice in the IL-17A-/- + Sev group compared with neonatal mice in Sev group. IL-17A deletion protects against long-term cognitive impairment induced by repeated sevoflurane exposure in neonatal mice. The underlying mechanism may relate to inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway as well as the reducing neuroinflammation.
Keywords: IL-17A; NF-κB signaling pathway; cognitive dysfunction; neuroinflammation; sevoflurane.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
IL-17A promotes the neuroinflammation and cognitive function in sevoflurane anesthetized aged rats via activation of NF-κB signaling pathway.BMC Anesthesiol. 2018 Oct 20;18(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0607-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 30342469 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A is a key regulator of neuroinflammation and neurodevelopment in cognitive impairment induced by sevoflurane.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Feb 1;227:12-26. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.11.039. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39581388
-
Resveratrol ameliorates sevoflurane-induced cognitive impairment by activating the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway in neonatal mice.J Nutr Biochem. 2021 Apr;90:108579. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108579. Epub 2020 Dec 31. J Nutr Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33388350
-
Repeated neonatal sevoflurane induced neurocognitive impairment through NF-κB-mediated pyroptosis.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Aug 21;18(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02233-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34419096 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of lncRNA MALAT1 Reduces LPS- or IL-17A-Induced Inflammatory Response in Human Middle Ear Epithelial Cells via the NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jan 6;2021:8844119. doi: 10.1155/2021/8844119. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33506040 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Surgery-induced neuroinflammatory transcriptional programs in medial prefrontal cortex of mice during early phase of perioperative neurocognitive disorders.PeerJ. 2024 Dec 3;12:e18664. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18664. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39650559 Free PMC article.
-
VISTA Alleviates Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation After Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Regulating ACOD1/Itaconic Acid Metabolism.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-05106-x. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40536592
References
-
- Sevoflurane. In: Drugs and lactation database (LactMed). Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); 2020.
-
- Fan XY, Shi G, Zhao P.. Neonatal sevoflurane exposure impairs learning and memory by the hypermethylation of hippocampal synaptic genes. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58:895–904. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
