Hearing loss in outbred Hartley guinea pigs experimentally infected with Pichinde virus as a surrogate model of human mammarenaviral hemorrhagic fevers
- PMID: 35758052
- PMCID: PMC9794012
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2087948
Hearing loss in outbred Hartley guinea pigs experimentally infected with Pichinde virus as a surrogate model of human mammarenaviral hemorrhagic fevers
Abstract
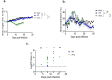
Lassa fever (LF) is a neglected tropical disease that is caused by Lassa virus (LASV), a human hemorrhagic fever-causing mammarenavirus. A notable sequela of LF is sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) that can develop in about 33% of the patients. Animal models of LF-associated SNHL have been limited in size and scope because LASV is a biosafety level 4 (BSL4) pathogen that requires its handling in a high biocontainment laboratory. In this report, we describe the development of an alternative arenavirus hearing loss model by infecting outbred Hartley guinea pigs with a virulent strain (rP18) of the Pichinde virus (PICV), which is a guinea pig-adapted mammarenavirus that has been used as a surrogate model of mammarenaviral hemorrhagic fevers in a conventional (BSL2) laboratory. By measuring auditory brainstem response (ABR) throughout the course of the virulent rP18 PICV infection, we noticed that some of the animals experienced an acute but transient level of hearing loss. Cochleae of hearing-impaired animals, but not of controls, had demonstrable viral RNA by quantitative RT-PCR, indicating the presence of virus in the affected inner ear with no overt histopathological changes. In contrast, neither the outbred Hartley guinea pigs infected with a known avirulent strain (rP2) of PICV nor those that were mock-infected showed any evidence of hearing loss or viral infection of the inner ear. This is the first report of an immunocompetent small animal model of mammarenavirus-induced hearing loss that can be used to evaluate potential therapeutics against virus-induced hearing impairment under a conventional laboratory setting.
Keywords: Arenavirus; Lassa virus; Mammarenavirus; Pichinde virus; Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL); Virus-induced hearing loss; guinea pigs.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Virulent infection of outbred Hartley guinea pigs with recombinant Pichinde virus as a surrogate small animal model for human Lassa fever.Virulence. 2020 Dec;11(1):1131-1141. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1809328. Virulence. 2020. PMID: 32799623 Free PMC article.
-
Pichinde Virus Infection of Outbred Hartley Guinea Pigs as a Surrogate Animal Model for Human Lassa Fever: Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Analyses.Pathogens. 2020 Jul 16;9(7):579. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9070579. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32708789 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Biological Role of Lassa Viral Z Protein-Mediated RIG-I Inhibition Using a Replication-Competent Trisegmented Pichinde Virus System in an Inducible RIG-IN Expression Cell Line.J Virol. 2022 Aug 24;96(16):e0075422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00754-22. Epub 2022 Aug 1. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35913216 Free PMC article.
-
Lassa fever-induced sensorineural hearing loss: A neglected public health and social burden.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Feb 22;12(2):e0006187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006187. eCollection 2018 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29470486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current small animal models for LASV hearing loss.Curr Opin Virol. 2019 Aug;37:118-122. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Curr Opin Virol. 2019. PMID: 31479989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of bi-segmented and tri-segmented recombinant Pichinde virus particles.J Virol. 2024 Oct 22;98(10):e0079924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00799-24. Epub 2024 Sep 12. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39264155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Günther S, Lenz O.. Lassa Virus. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2004;41:339–390. - PubMed
-
- Efficacy trials of Lassa Therapeutics: endpoints, trial design, site selection [Internet] . Paris, France: WHO Workshop; 2018. [cited 2021 Nov 17]. Available from: https://www.who.int/blueprint/what/norms-standards/LassaTxeval_Finalmeet...
-
- McCormick JB. Encyclopedia of Virology. 3rd ed. Academic Press; 2008.
-
- Prioritizing diseases for research and development in emergency contexts.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
