Toll-like receptor 3 gene regulates cataract-related mechanisms via the Jagged-1/Notch signaling pathway
- PMID: 35758265
- PMCID: PMC9342145
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2085391
Toll-like receptor 3 gene regulates cataract-related mechanisms via the Jagged-1/Notch signaling pathway
Abstract
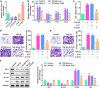
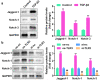
Epithelial-melancholy transition (EMT) is the main cause of organ fibrosis and a common pathogenetic mechanism in most cataracts. This study aimed to explore the molecular mechanism of Toll-like receptor (TLR)-3 in the occurrence and development of post-cataract EMT and to provide new ideas for the prevention and treatment of posterior capsule opacification (PCO). In the presence or absence of TLR3, the human lens epithelial cell (LEC) line, SRA01/04, was treated with the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β2. Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and Transwell assays were used to analyze the cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. The expression levels of proteins and RNAs were detected by western blotting and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) experiments. Functional gain and loss studies showed that TLR3 regulates the proliferation, migration, and invasion of LECs and EMT induced by TGF-β2. Moreover, TLR3 regulates the expression of Jagged-1, Notch-1, and Notch-3 These findings indicate that TLR3 prevents the progression of lens fibrosis by targeting the Jagged-1/Notch signaling pathway to regulate the proliferation, migration, and invasion of LECs, and TGF-β2-induced EMT. Therefore, the TLR3-Jagged-1/Notch signaling axis may be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of fibrotic cataracts.
Keywords: EMT; Jagged-1/Notch signaling pathway; TLR3; fibrotic cataract.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





Similar articles
-
CtBP2 Regulates TGFβ2-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Through Notch Signaling Pathway in Lens Epithelial Cells.Curr Eye Res. 2016 Aug;41(8):1057-1063. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2015.1092554. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Curr Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26681554
-
MicroRNA-26a and -26b inhibit lens fibrosis and cataract by negatively regulating Jagged-1/Notch signaling pathway.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Aug;24(8):1431-1442. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.152. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28622289 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0000099/miR-223-3p/CTGF Regulates the Growth, Metastasis, and EMT Processes in TGF-β2-Stimulated Human Lens Epithelial Cells.Curr Eye Res. 2024 Oct;49(10):1042-1053. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2024.2357600. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Curr Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38940233
-
Blockade of Jagged/Notch pathway abrogates transforming growth factor β2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human retinal pigment epithelium cells.Curr Mol Med. 2014 May;14(4):523-34. doi: 10.2174/1566524014666140331230411. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24694299 Review.
-
Fibrosis in the lens. Sprouty regulation of TGFβ-signaling prevents lens EMT leading to cataract.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Jan;142:92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 May 21. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26003864 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-viral gene coating modified IOL delivering PDGFR-α shRNA interferes with the fibrogenic process to prevent posterior capsular opacification.Regen Biomater. 2023 Mar 8;10:rbad020. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbad020. eCollection 2023. Regen Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36950659 Free PMC article.
-
Mannose-binding lectin suppresses macrophage proliferation through TGF-β1 signaling pathway in Nile tilapia.Front Immunol. 2023 May 16;14:1159577. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1159577. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37261343 Free PMC article.
-
ceRNA network construction and identification of hub genes as novel therapeutic targets for age-related cataracts using bioinformatics.PeerJ. 2023 Mar 23;11:e15054. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15054. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36987450 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathways in age-related eye disease: from mechanisms to targeted therapeutics.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Aug 19. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01913-9. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40828357 Review.
References
-
- Wang W, Yan W, Fotis K, et al. Cataract surgical rate and socioeconomics: a global study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(14):5872–5881. - PubMed
-
- Yan W, Wang W, Wijngaarden P, et al. Longitudinal changes in global cataract surgery rate inequality and associations with socioeconomic indices. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019;47(4):453–460. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
