The latent period of coronavirus disease 2019 with SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant of concern in the postvaccination era
- PMID: 35759239
- PMCID: PMC9186332
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.664
The latent period of coronavirus disease 2019 with SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant of concern in the postvaccination era
Abstract
Introduction: Emerging variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) have resulted in new challenges for epidemic prevention and control worldwide. However, little is known about the latent period of coronavirus disease by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant of concern (VOC) in the postvaccination era.
Methods: The epidemiology and clinical data of cases with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC infection were retrospective collected. Dates of the first positive PCR test were collected to estimate the distribution of latent period.
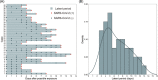
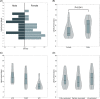
Results: Of the 40 patients, 16 were male (40%). The median age of patients was 47.5 years. The median latent period of patients was 6.0 days (interquartile range [IQR], 4.0-9.0 days) and the longest latent period was 13.0 days after exposure. The latent periods were longer in male patients compared to female patients (median, 8.5 days vs. 5.0 days, p = .041). The median latent period was comparable among fully vaccinated cases (6.5 days), no vaccinated cases (7.5 days), and partially vaccinated cases (5.5 days).
Conclusions: The median latent period of SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC infection was 6.0 days. The latent period between vaccinated and non-vaccinated patients was not significantly different. The 14-day quarantine program is sufficient to prevent the transmission of COVID-19 by Delta VOC in the postvaccination era.
Keywords: latent period; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; vaccine; variant of concern.
© 2022 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID‐19 – 11 May 2021. May 11, 2021. Accessed November 8, 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on...
-
- Fine PE. The interval between successive cases of an infectious disease. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;158(11):1039‐1047. - PubMed
-
- Xin H, Li Y, Wu P, et al. Estimating the latent period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19). Clin Infect Dis. 2022;74(9):1678‐1681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

