Pooled incidence and case-fatality of acute stroke in Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macao: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35759497
- PMCID: PMC9236238
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270554
Pooled incidence and case-fatality of acute stroke in Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macao: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Stroke incidence and case-fatality in Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macao vary by geographic region and rates often differ across and within regions. This systematic review and meta-analysis (SR) estimated the pooled incidence and short-term case-fatality of acute first ever stroke in mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macao.
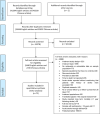
Methods: Longitudinal studies published in English or Chinese after 1990 were searched in PubMed/Medline, EMBASE, CINAHL, Web of Science, SinoMed and CQVIP. The incidence was expressed as Poisson means estimated as the number of events divided by time at risk. Random effect models calculated the pooled incidence and pooled case-fatality. Chi-squared trend tests evaluated change in the estimates over time. When possible, age standardised rates were calculated. Percent of variation across studies that was due to heterogeneity rather than chance was tested using the I2 statistic.The effect of covariates on heterogeneity was investigated using meta-regressions. Publication bias was tested using funnel plots and Egger's tests.
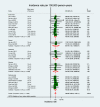
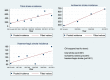
Results: Overall, 72 studies were included. The pooled incidences of total stroke (TS), ischaemic stroke (IS) and haemorrhagic stroke (HS) were 468.9 (95% confidence interval (CI): 163.33-1346.11), 366.79 (95% CI: 129.66-1037.64) and 106.67 (95% CI: 55.96-203.33) per 100,000 person-years, respectively, varied according to the four economic regions (East Coast, Central China, Northeast and Western China) with the lowest rates detected in the East Coast. Increased trends over time in the incidence of TS and IS were observed (p<0.001 in both). One-month and three-to-twelve-month case-fatalities were 0.11 (95% CI: 0.04-0.18) and 0.15 (95% CI: 0.12-0.17), respectively for IS; and 0.36 (95% CI: 0.26-0.45) and 0.25 (95% CI: 0.18-0.32), respectively for HS. One-month case-fatality of IS and HS decreased over time for both (p<0.001). Three-to-twelve-month fatalities following IS increased over time (p<0.001). Publication bias was not found.
Conclusions: Regional differences in stroke incidence were observed with the highest rates detected in less developed regions. Although 1-month fatality following IS is decreasing, the increased trends in 3-12-month fatality may suggest an inappropriate long-term management following index hospital discharge.
Registration: Registration-URL: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/; Reference code: CRD42020170724.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Geographical Disparities in Pooled Stroke Incidence and Case Fatality in Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macao: Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JMIR Res Protoc. 2022 Jan 18;11(1):e32566. doi: 10.2196/32566. JMIR Res Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35040797 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric stroke among Hong Kong Chinese subjects.Pediatrics. 2004 Aug;114(2):e206-12. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.2.e206. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15286258
-
Prevalence of depression and its relationship with quality of life among university students in Macau, Hong Kong and mainland China.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 25;10(1):15798. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72458-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32978428 Free PMC article.
-
Stroke case fatality in sub-Saharan Africa: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Stroke. 2021 Oct;16(8):902-916. doi: 10.1177/1747493021990945. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Int J Stroke. 2021. PMID: 33527885
-
Global incidence and risk factors for glaucoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies.J Glob Health. 2024 Nov 8;14:04252. doi: 10.7189/jogh.14.04252. J Glob Health. 2024. PMID: 39513294 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Delayed inpatient rehabilitation and functional outcomes for acute stroke: a retrospective cohort study in an Australian regional hospital.J Rehabil Med. 2025 Aug 5;57:jrm42506. doi: 10.2340/jrm.v57.42506. J Rehabil Med. 2025. PMID: 40762230 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

