The global health workforce stock and distribution in 2020 and 2030: a threat to equity and 'universal' health coverage?
- PMID: 35760437
- PMCID: PMC9237893
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2022-009316
The global health workforce stock and distribution in 2020 and 2030: a threat to equity and 'universal' health coverage?
Abstract
Objective: The 2016 Global Strategy on Human Resources for Health: Workforce 2030 projected a global shortage of 18 million health workers by 2030. This article provides an assessment of the health workforce stock in 2020 and presents a revised estimate of the projected shortage by 2030.
Methods: Latest data reported through WHO's National Health Workforce Accounts (NHWA) were extracted to assess health workforce stock for 2020. Using a stock and flow model, projections were computed for the year 2030. The global health workforce shortage estimation was revised.
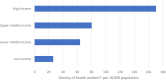
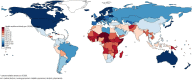
Results: In 2020, the global workforce stock was 29.1 million nurses, 12.7 million medical doctors, 3.7 million pharmacists, 2.5 million dentists, 2.2 million midwives and 14.9 million additional occupations, tallying to 65.1 million health workers. It was not equitably distributed with a 6.5-fold difference in density between high-income and low-income countries. The projected health workforce size by 2030 is 84 million health workers. This represents an average growth of 29% from 2020 to 2030 which is faster than the population growth rate (9.7%). This reassessment presents a revised global health workforce shortage of 15 million health workers in 2020 decreasing to 10 million health workers by 2030 (a 33% decrease globally). WHO African and Eastern Mediterranean regions' shortages are projected to decrease by only 7% and 15%, respectively.
Conclusions: The latest NHWA data show progress in the increasing size of the health workforce globally as more jobs are and will continue to be created in the health economy. It however masks considerable inequities, particularly in WHO African and Eastern Mediterranean regions, and alarmingly among the 47 countries on the WHO Support and Safeguards List. Progress should be acknowledged with caution considering the immeasurable impact of COVID-19 pandemic on health workers globally.
Keywords: descriptive study; health systems evaluation; medical demography; public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Second round of the national pulse survey on continuity of essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2021.
-
- Campbell J, Dussault G, Buchan J, et al. A universal truth: no health without a workforce. Geneva: Global Health Workforce Alliance and World Health Organization, 2013.
-
- WHO . Global strategy on human resources for health: workforce 2030. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/250368/1/9789241511131-eng.pdf
-
- WHO . National health workforce accounts: a Handbook. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2017. http://www.who.int/hrh/documents/brief_nhwa_handbook/en/
-
- WHO . State of the world’s nursing 2020: investing in education, jobs and leadership. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240003279
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
