Assessment of the frequency of coughing and sneezing triggered by nasopharyngeal swabbing in the pandemic setting
- PMID: 35760972
- PMCID: PMC9237027
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-14755-0
Assessment of the frequency of coughing and sneezing triggered by nasopharyngeal swabbing in the pandemic setting
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Assessment of the frequency of coughing and sneezing triggered by nasopharyngeal swabbing in the pandemic setting.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 18;12(1):12271. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16684-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35851314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
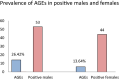
A variety of medical procedures are classified as aerosol generating. However there is no consensus on whether some procedures such as nasopharyngeal swabbing can generate aerosols. During specimen collection, the contact of the nasopharyngeal swab with the respiratory mucosa often triggers defense reflexes such as sneezing and coughing, which generate airborne particles. The accumulation and persistence of a viral load from infectious aerosols for hours after their generation can represent a threat for increased spread of infection. Prospective observational cohort study in individuals tested for RT-PCR SARS-CoV-2 from July to October 2020. Participants were evaluated for the prevalence of aerosol generating events (AGEs) triggered by the nasopharyngeal swabbing. We used descriptive statistics to analyze the data set and the chi-square test for AGE comparison between sexes. Among 1239 individuals, we reported 264 in which AGEs were triggered by the specimen collection. 97 individuals tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, of which 20 presented AGEs. There were no significant differences in the occurrence of AGEs by age, but significant differences have been identified between sex and the occurrence of AGEs both in the SARS-CoV-2 negative and SARS-CoV-2 positive individuals. The prevalence of coughing or sneezing triggered by the nasopharyngeal swabbing was high among tested individuals. Testing facilities should ensure adequate availability of personal protective equipment (PPE) for the testing personnel, ensure appropriate ventilation of the rooms, and develop additional strategies to limit the risk of contamination of other participants to the testing session from potentially infectious and persistent aerosols.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Atkinson, J, et al. Respiratory droplets. 2009; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK143281/. Accessed 23 Sept 2020.
-
- Flügge C. Ueber Luftinfection. Z. Hyg Infekt. 1997;25:179–224. doi: 10.1007/BF02220473. - DOI
-
- Jennison MW. Atomizing of mouth and nose secretions into the air as revealed by high-speed photography. In: Moulton FR, editor. Aerobiology. American Association for the Advancement of Science; 1942. pp. 106–128.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

