Role of exosomes in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of central nervous system diseases
- PMID: 35761337
- PMCID: PMC9235237
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-022-03493-6
Role of exosomes in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of central nervous system diseases
Abstract
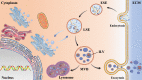
Central nervous system (CNS) diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease (AD), and Parkinson's disease (PD), affect millions of people around the world. Great efforts were put in disease related research, but few breakthroughs have been made in the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Exosomes are cell-derived extracellular vesicles containing diverse biologically active molecules secreted by their cell of origin. These contents, including nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, amino acids, and metabolites, can be transferred between different cells, tissues, or organs, regulating various intercellular cross-organ communications and normal and pathogenic processes. Considering that cellular environment and cell state strongly impact the content and uptake efficiency of exosomes, their detection in biological fluids and content composition analysis potentially offer a multicomponent diagnostic readout of several human diseases. Recently, studies have found that aberrant secretion and content of exosomes are closely related to the pathogenesis of CNS diseases. Besides, loading natural cargoes, exosomes can deliver drugs cross the blood brain barrier, making them emerging candidates of biomarkers and therapeutics for CNS diseases. In this review, we summarize and discuss the advanced research progress of exosomes in the pathological processes of several CNS diseases in regarding with neuroinflammation, CNS repair, and pathological protein aggregation. Moreover, we propose the therapeutic strategies of applying exosomes to the diagnosis, early detection, and treatment of CNS diseases.
Keywords: Biomarkers; CNS; Central nervous system diseases; Exosomes; Nerve injury repair.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

