DUAL I China: Improved glycemic control with IDegLira versus its individual components in a randomized trial with Chinese participants with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic drugs
- PMID: 35762390
- PMCID: PMC9366571
- DOI: 10.1111/1753-0407.13286
DUAL I China: Improved glycemic control with IDegLira versus its individual components in a randomized trial with Chinese participants with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic drugs
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Vox Sang. 2022 Oct;117(10):1242. doi: 10.1111/vox.13360. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Vox Sang. 2022. PMID: 36125918 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Corrigendum.J Diabetes. 2022 Sep;14(9):635-637. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13307. J Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 36163590 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: DUAL I China, one of the DUAL trials, assessed efficacy/safety of insulin degludec/liraglutide (IDegLira) in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) not controlled by oral antidiabetic drugs (OADs).
Methods: This phase 3a, treat-to-target multicenter trial randomized participants (glycated hemoglobin [HbA1c] 53.0-85.8 mmol/mol; previous metformin ± another OAD) 2:1:1 to IDegLira (n = 361), degludec (n = 179), or liraglutide (n = 180). Primary endpoint was change in HbA1c after 26 weeks. Secondary endpoints included: HbA1c < 53.0 mmol/mol attainment, weight change, treatment-emergent hypoglycemia, end-of-treatment insulin dose, and safety.
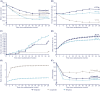
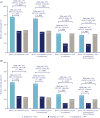
Results: At 26 weeks, HbA1c had decreased by a mean 18.12 mmoL/moL (IDegLira), 12.37 mmoL/moL (degludec) (estimated treatment difference [ETD] -6.50 mmoL/moL; 95% confidence interval [CI] -7.96, -5.04; P < .0001), and 11.33 mmoL/moL (liraglutide) (ETD -6.87 mmoL/moL; 95% CI -8.33, -5.41; P < 0.0001), indicating noninferiority for IDegLira vs degludec and superiority vs liraglutide. HbA1c < 53.0 mmoL/moL attainment was 77.0% (IDegLira), 46.4% (degludec), and 48.3% (liraglutide). Mean weight change with IDegLira (0.1 kg) was superior to degludec (1.2 kg) (ETD -1.08 kg; 96% CI -1.55, -0.62; P < 0.0001). Severe or confirmed hypoglycemic event rates were 0.24 (IDegLira) and 0.17 (degludec) episodes/participant-year (estimated rate ratio 1.46; 95% CI 0.71, 3.02; P = .3008, not significant). At the end of treatment, the IDegLira insulin dose was lower (24.5 U/d) vs degludec (30.3 U/d) (ETD -5.49 U; 95% CI -7.77, -3.21; P < 0.0001). No unexpected safety issues occurred.
Conclusions: IDegLira is efficacious and well tolerated in Chinese adults with T2D not controlled by OADs.
背景: 作为DUAL试验之一的DUAL I China评估了未口服抗糖药物(OADs)控制血糖的中国成人2型糖尿病(T2D)患者应用德谷胰岛素/利拉鲁肽(IDegLira)的有效性/安全性。 方法: 这项3a期, 治疗导向的多中心随机对照试验中, 受试者糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)为53.0-85.8 mmol/mol, 之前治疗为二甲双胍配合或不配合其他口服抗糖药物。按2:1:1的比例分别给予IDegLira(n=361), 德谷胰岛素(n=179)或利拉鲁肽(n=180)。主要终点是26周后HbA1c的变化。次要终点包括:HbA1c<53.0 mmol/mol, 体重变化, 治疗后出现的低血糖, 治疗结束时的胰岛素剂量, 以及安全性。 结果: 治疗26周时, 糖化血红蛋白平均下降18.12mmol/mol(IDegLira), 12.37mmol/mol(德谷胰岛素)(治疗前后差值估计(ETD)为-6.50 mmoL/m ol, 95%可信区间−7.96, −5.04, P<0.0001)和11.33 mmoL/mol(利拉鲁肽)(ETD−6.87 mmoL/mol, 95%置信区间−8.33, −5.41, P<0.0001), 表明IDegLira相对于德谷胰岛素的非劣效性, 以及相对于利拉鲁肽的优越性。糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)的达标率为77.0%(IDegLira), 46.4%(德谷胰岛素)和48.3%(利拉鲁肽)。平均体重变化:IDegLira组(0.1 kg)优于德谷胰岛素组(1.2 kg), ETD为-1.08 kg(95%CI−1.5 5, −0.62), P<0.001。严重或确认的低血糖事件发生率分别为0.24(IDegLira)和0.17(德谷胰岛素)次/参与者-年, 估计比率为1.46(95%CI:0.71, 3.02), P=.3008, 无显著意义。治疗结束时, IDegLira胰岛素剂量(24.5U/天)低于德谷胰岛素(30.3U/天), ETD为-5.49U[95%CI:−7.77, −3.21], P<0.0001。没有发生意外安全事件。 结论: IDegLira治疗非OADs控制的中国成人T2D是有效的且耐受性良好。.
Keywords: 2型糖尿病; Chinese; clinical trial; insulin; liraglutide; type 2 diabetes; 中国; 临床试验; 利拉鲁肽; 胰岛素.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes published by Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- IDF . IDF Diabetes Atlas 9th Edition 2019. Accessed December2, 2019. https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/resources/
-
- Jia W, Weng J, Zhu D, et al. Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2019;2019:e3158. - PubMed
-
- Kim YG, Hahn S, Oh TJ, Kwak SH, Park KS, Cho YM. Differences in the glucose‐lowering efficacy of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors between Asians and non‐Asians: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Diabetologia. 2013;56:696‐708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

