Real-world utilization of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with palliative radiotherapy in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35762488
- PMCID: PMC9376180
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.14553
Real-world utilization of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with palliative radiotherapy in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade plus radiotherapy may be a promising strategy to improve the prognosis of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the optimum combined scheme, treatment time of radiotherapy, and irradiated lesion have not been fully determined.
Methods: A total of 321 metastatic NSCLC patients treated with immunotherapy were identified. Among them, 107 patients received PD-1/PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitors with radiotherapy, while the remaining cases did not receive radiotherapy. Data on overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), treatment response and adverse events were collected. Comparisons based on type of radiation, timing of radiotherapy and number of irradiated lesions were performed.
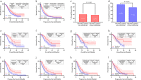
Results: The median OS in PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus radiotherapy was longer than in nonradiotherapy (22.8 vs. 16.6 months, p = 0.022). The median PFS showed a similar trend in this study (9.4 vs. 6.2 months, p = 0.042). Moreover, the combined strategy demonstrated a superior disease control rate and abscopal control rate versus without radiotherapy (both p ≤ 0.001). Further multivariate analysis in the immunotherapy and radiotherapy groups revealed that age below 65 (p = 0.004), Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance scores of 0-1 (p = 0.001), oligometastasis (p = 0.006), concurrent combination (p = 0.002), and treated with SRT (p = 0.013) were associated with longer OS. There was a similar incidence of adverse events between the two groups (both p ≥ 0.05).
Conclusions: The combination of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus palliative radiotherapy demonstrated favorable survival and good tolerability in metastatic NSCLC patients.
Keywords: immunotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer; radiotherapy.
© 2022 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and Efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with radiotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2021 Feb;10(4):1222-1239. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3718. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33465302 Free PMC article.
-
[Real-world study on the efficacy and prognostic predictive biomarker of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer treated with programmed death-1/programmed death ligand 1 inhibitors].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022 May 23;44(5):416-424. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20210709-00504. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35615798 Chinese.
-
Real-world evidenceand clinical observations of the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 12;9(1):4278. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40748-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30862891 Free PMC article.
-
Fostering efficacy of anti-PD-1-treatment: Nivolumab plus radiotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer - study protocol of the FORCE trial.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 8;19(1):1074. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6205-0. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31703637 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
SBRT combined with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in NSCLC treatment: a focus on the mechanisms, advances, and future challenges.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Jul 28;13(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00940-z. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32723363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of thoracic radiotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer patients receiving first-line immunotherapy plus chemotherapy: a propensity score matched multicentre retrospective analysis.Radiat Oncol. 2024 Feb 27;19(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02420-x. Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38413988 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Anlotinib Combined with PD-1 Blockades in Patients with Previously Immunotherapy Treated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Exploratory Study.Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2024 Mar 25;15:29-40. doi: 10.2147/LCTT.S444884. eCollection 2024. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 38560413 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased risk of radiation pneumonitis with concurrent use of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in thoracic radiation therapy of lung cancer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 12;10:1255786. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1255786. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37901395 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint blockers (ICB) and radiotherapy combination versus ICB in non-small cell lung cancer patients with recurrence or metastasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2023 Jul;12(13):13928-13941. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5958. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37323098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Proto C, Ferrara R, Signorelli D, Lo Russo G, Galli G, Imbimbo M, et al. Choosing wisely first line immunotherapy in non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): what to add and what to leave out. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019;75:39–51. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi L, Rodriguez‐Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(22):2078–92. - PubMed
-
- West H, McCleod M, Hussein M, Morabito A, Rittmeyer A, Conter HJ, et al. Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus nab‐paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as first‐line treatment for metastatic non‐squamous non‐small‐cell lung cancer (IMpower130): a multicentre, randomised, open‐label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(7):924–37. - PubMed
-
- Paz‐Ares L, Vicente D, Tafreshi A, Robinson A, Soto Parra H, Mazieres J, et al. A randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in patients with metastatic squamous NSCLC: protocol‐specified final analysis of KEYNOTE‐407. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15(10):1657–69. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

