Imaging Clostridioides difficile Spore Germination and Germination Proteins
- PMID: 35762766
- PMCID: PMC9295549
- DOI: 10.1128/jb.00210-22
Imaging Clostridioides difficile Spore Germination and Germination Proteins
Abstract
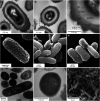
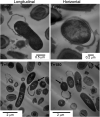
Clostridioides difficile spores are the infective form for this endospore-forming organism. The vegetative cells are intolerant to oxygen and poor competitors with a healthy gut microbiota. Therefore, in order for C. difficile to establish infection, the spores have to germinate in an environment that supports vegetative growth. To initiate germination, C. difficile uses Csp-type germinant receptors that consist of the CspC and CspA pseudoproteases as the bile acid and cogerminant receptors, respectively. CspB is a subtilisin-like protease that cleaves the inhibitory propeptide from the pro-SleC cortex lytic enzyme, thereby activating it and initiating cortex degradation. Though several locations have been proposed for where these proteins reside within the spore (i.e., spore coat, outer spore membrane, cortex, and inner spore membrane), these have been based, mostly, on hypotheses or prior data in Clostridium perfringens. In this study, we visualized the germination and outgrowth process using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and used immunogold labeling to visualize key germination regulators. These analyses localize these key regulators to the spore cortex region for the first time. IMPORTANCE Germination by C. difficile spores is the first step in the establishment of potentially life-threatening C. difficile infection (CDI). A deeper understanding of the mechanism by which spores germinate may provide insight for how to either prevent spore germination into a disease-causing vegetative form or trigger germination prematurely when the spore is either in the outside environment or in a host environment that does not support the establishment of colonization/disease.
Keywords: Clostridium difficile; cortex; endospores; germination; imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Jump RL, Pultz MJ, Donskey CJ. 2007. Vegetative Clostridium difficile survives in room air on moist surfaces and in gastric contents with reduced acidity: a potential mechanism to explain the association between proton pump inhibitors and C. difficile-associated diarrhea? Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:2883–2887. doi:10.1128/AAC.01443-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buffie CG, Bucci V, Stein RR, McKenney PT, Ling L, Gobourne A, No D, Liu H, Kinnebrew M, Viale A, Littmann E, van den Brink MR, Jenq RR, Taur Y, Sander C, Cross JR, Toussaint NC, Xavier JB, Pamer EG. 2015. Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile. Nature 517:205–208. doi:10.1038/nature13828. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Theriot CM, Koenigsknecht MJ, Carlson PE, Jr, Hatton GE, Nelson AM, Li B, Huffnagle GB, Li JZ, Young VB. 2014. Antibiotic-induced shifts in the mouse gut microbiome and metabolome increase susceptibility to Clostridium difficile infection. Nat Commun 5:3114. doi:10.1038/ncomms4114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

