Discovery of the First-in-Class G9a/GLP Covalent Inhibitors
- PMID: 35763668
- PMCID: PMC9482816
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00652
Discovery of the First-in-Class G9a/GLP Covalent Inhibitors
Abstract
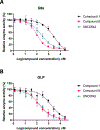
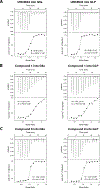
The highly homologous protein lysine methyltransferases G9a and GLP, which catalyze mono- and dimethylation of histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9), have been implicated in various human diseases. To investigate functions of G9a and GLP in human diseases, we and others reported several noncovalent reversible small-molecule inhibitors of G9a and GLP. Here, we report the discovery of the first-in-class G9a/GLP covalent irreversible inhibitors, 1 and 8 (MS8511), by targeting a cysteine residue at the substrate binding site. We characterized these covalent inhibitors in enzymatic, mass spectrometry based and cellular assays and using X-ray crystallography. Compared to the noncovalent G9a/GLP inhibitor UNC0642, covalent inhibitor 8 displayed improved potency in enzymatic and cellular assays. Interestingly, compound 8 also displayed potential kinetic preference for covalently modifying G9a over GLP. Collectively, compound 8 could be a useful chemical tool for studying the functional roles of G9a and GLP by covalently modifying and inhibiting these methyltransferases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): J.J. is a cofounder and equity shareholder in Cullgen Inc. and a consultant for Cullgen Inc., EpiCypher Inc., and Accent Therapeutics Inc. The Jin laboratory received research funds from Celgene Corporation, Levo Therapeutics, Cullgen, Inc. and Cullinan Oncology
Figures









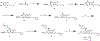
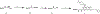
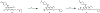
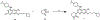
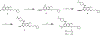
References
-
- Hamamoto R; Saloura V; Nakamura Y Critical roles of non-histone protein lysine methylation in human tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15 (2), 110–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

