Humoral and cellular immune memory to four COVID-19 vaccines
- PMID: 35764089
- PMCID: PMC9135677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.05.022
Humoral and cellular immune memory to four COVID-19 vaccines
Abstract
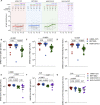
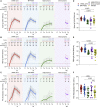
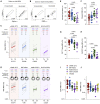
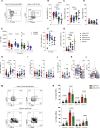
Multiple COVID-19 vaccines, representing diverse vaccine platforms, successfully protect against symptomatic COVID-19 cases and deaths. Head-to-head comparisons of T cell, B cell, and antibody responses to diverse vaccines in humans are likely to be informative for understanding protective immunity against COVID-19, with particular interest in immune memory. Here, SARS-CoV-2-spike-specific immune responses to Moderna mRNA-1273, Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2, Janssen Ad26.COV2.S, and Novavax NVX-CoV2373 were examined longitudinally for 6 months 100% of individuals made memory CD4+ T cells, with cTfh and CD4-CTL highly represented after mRNA or NVX-CoV2373 vaccination. mRNA vaccines and Ad26.COV2.S induced comparable CD8+ T cell frequencies, though only detectable in 60-67% of subjects at 6 months. A differentiating feature of Ad26.COV2.S immunization was a high frequency of CXCR3+ memory B cells. mRNA vaccinees had substantial declines in antibodies, while memory T and B cells were comparatively stable. These results may also be relevant for insights against other pathogens.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; SARS-COV2; cellular immunity; humoral immunity; immune memory.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.S. is a consultant for Gritstone Bio, Flow Pharma, ImmunoScape, Avalia, Moderna, Fortress, Repertoire, Gerson Lehrman Group, RiverVest, MedaCorp, and Guggenheim. S.C. has consulted for GSK, JP Morgan, Citi, Morgan Stanley, Avalia NZ, Nutcracker Therapeutics, University of California, California State Universities, United Airlines, Adagio, and Roche. LJI has filed for patent protection for various aspects of T cell epitope and vaccine design work. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











Update of
-
Humoral and cellular immune memory to four COVID-19 vaccines.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Mar 21:2022.03.18.484953. doi: 10.1101/2022.03.18.484953. bioRxiv. 2022. Update in: Cell. 2022 Jul 7;185(14):2434-2451.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.05.022. PMID: 35350195 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

