High frequency of anti-DSG 2 antibodies in post COVID-19 serum samples
- PMID: 35764120
- PMCID: PMC9233549
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2022.06.006
High frequency of anti-DSG 2 antibodies in post COVID-19 serum samples
Abstract
Background: There is growing recognition that COVID-19 does cause cardiac sequelae. The underlying mechanisms involved are still poorly understood to date. Viral infections, including COVID-19, have been hypothesized to contribute to autoimmunity, by exposing previously hidden cryptic epitopes on damaged cells to an activated immune system. Given the high incidence of cardiac involvement seen in COVID-19, our aim was to determine the frequency of anti-DSG2 antibodies in a population of post COVID-19 patients.
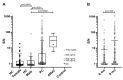
Methods and results: 300 convalescent serum samples were obtained from a group of post COVID-19 infected patients from October 2020 to February 2021. 154 samples were drawn 6 months post-COVID-19 infection and 146 samples were drawn 9 months post COVID infection. 17 samples were obtained from the same patient at the 6- and 9- month mark. An electrochemiluminescent-based immunoassay utilizing the extracellular domain of DSG2 for antibody capture was used. The mean signal intensity of anti-DSG2 antibodies in the post COVID-19 samples was significantly higher than that of a healthy control population (19 ± 83.2 in the post-COVID-19 sample vs. 2.1 ± 7.2 (p < 0. 0001) in the negative control healthy population). Of note, 29.3% of the post COVID-19 infection samples demonstrated a signal higher than the 90th percentile of the control population and 8.7% were higher than the median found in ARVC patients. The signal intensity between the 6-month and 9-month samples did not differ significantly.
Conclusions: We report for the first time that recovered COVID-19 patients demonstrate significantly higher and sustained levels of anti-DSG2 autoantibodies as compared to a healthy control population, comparable to that of a diagnosed ARVC group.
Keywords: ARVC; Anti DSG2 antibody; COVID 19; Cardiomyopathy.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with anti-desmoglein 2 autoantibody detection.Clin Exp Immunol. 2023 Jul 21;213(2):243-251. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad046. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37095599 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Correlates of Anti-DSG2 Antibodies in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis: Immunological Insights from a Multicenter Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 8;13(22):6736. doi: 10.3390/jcm13226736. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39597880 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies against Spike protein correlate with broad autoantigen recognition 8 months post SARS-CoV-2 exposure, and anti-calprotectin autoantibodies associated with better clinical outcomes.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 11;13:945021. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.945021. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032086 Free PMC article.
-
Dsg2 Upregulation as a Rescue Mechanism in Pemphigus.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 28;11:581370. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.581370. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193387 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Mystery Surrounding Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 30;12:686029. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.686029. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276671 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exome-Wide Association Study Reveals Host Genetic Variants Likely Associated with the Severity of COVID-19 in Patients of European Ancestry.Life (Basel). 2022 Aug 24;12(9):1300. doi: 10.3390/life12091300. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36143338 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of autoantibodies to desmoglein-2 in dogs with and without cardiac disease.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 28;13(1):5044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32081-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36977772 Free PMC article.
-
The immunology of long COVID.Nat Rev Immunol. 2023 Oct;23(10):618-634. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00904-7. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37433988 Review.
-
Translating insights into therapies for Long Covid.Sci Transl Med. 2024 Nov 13;16(773):eado2106. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.ado2106. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Sci Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39536116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding autoimmune response after SARS-CoV-2 infection and the pathogenesis/mechanisms of long COVID.Med Rev (2021). 2024 May 27;4(5):367-383. doi: 10.1515/mr-2024-0013. eCollection 2024 Oct. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 39444797 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collection of ARVC serum by Arvada Therapeutics under ICH guidelines. 2022.
-
- Wang E.Y., Mao T., Klein J., Dai Y., Huck J.D., Jaycox J.R., et al. Diverse functional autoantibodies in patients with COVID-19. Nature Res. 2021;595:283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

