Beneficial Effects of the Direct AMP-Kinase Activator PXL770 in In Vitro and In Vivo Models of X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy
- PMID: 35764327
- PMCID: PMC11047065
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.122.001208
Beneficial Effects of the Direct AMP-Kinase Activator PXL770 in In Vitro and In Vivo Models of X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy
Abstract
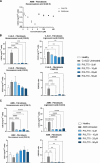
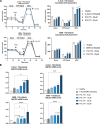
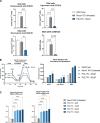
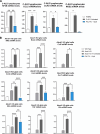
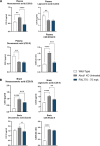
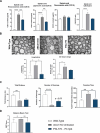
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a severe orphan disease caused by mutations in the peroxisomal ABCD1 transporter gene, leading to toxic accumulation of Very Long-Chain Fatty Acids (VLCFA - in particular C26:0) resulting in inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction and demyelination. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is downregulated in ALD, and its activation is implicated as a therapeutic target. PXL770 is the first direct allosteric AMPK activator with established clinical efficacy and tolerability.
Copyright © 2022 by The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metformin-induced mitochondrial function and ABCD2 up-regulation in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy involves AMP-activated protein kinase.J Neurochem. 2016 Jul;138(1):86-100. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13562. Epub 2016 Mar 14. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 26849413
-
Therapeutic potential of deuterium-stabilized (R)-pioglitazone-PXL065-for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2022 Jul;45(4):832-847. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12510. Epub 2022 May 19. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2022. PMID: 35510808 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces adrenoleukodystrophy (Abcd2) gene in human X-ALD fibroblasts and inhibits the proinflammatory response in Abcd1/2 silenced mouse primary astrocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Apr;1831(4):747-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23318275 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical aspects of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Brain Pathol. 2010 Jul;20(4):831-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2010.00391.x. Brain Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20626744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting the Pathogenesis of X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy.Genes (Basel). 2025 May 17;16(5):590. doi: 10.3390/genes16050590. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathophysiology of X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: Updates on Molecular Mechanisms.J Biotechnol Biomed. 2024;7(2):277-288. doi: 10.26502/jbb.2642-91280151. Epub 2024 Jun 14. J Biotechnol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39056013 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into activation and function of the AMPK.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Apr;24(4):255-272. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00547-x. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36316383 Review.
-
The role of CNBP in brain atrophy and its targeting in myotonic dystrophy type 2.Hum Mol Genet. 2025 Mar 7;34(6):512-522. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaf002. Hum Mol Genet. 2025. PMID: 39807631
-
Role of the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway in non‑alcoholic fatty liver disease (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2023 Feb;27(2):35. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12922. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36562343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asheuer M, Bieche I, Laurendeau I, Moser A, Hainque B, Vidaud M, Aubourg P (2005) Decreased expression of ABCD4 and BG1 genes early in the pathogenesis of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet 14:1293–1303. - PubMed
-
- Beirowski B, Berek L, Adalbert R, Wagner D, Grumme DS, Addicks K, Ribchester RR, Coleman MP (2004) Quantitative and qualitative analysis of Wallerian degeneration using restricted axonal labelling in YFP-H mice. J Neurosci Methods 134:23–35. - PubMed
-
- Bezman L, Moser AB, Raymond GV, Rinaldo P, Watkins PA, Smith KD, Kass NE, Moser HW (2001) Adrenoleukodystrophy: incidence, new mutation rate, and results of extended family screening. Ann Neurol 49:512–517. - PubMed
-
- Cusi KAlkhouri NHarrison SAFouqueray PMoller DEHallakou-Bozec SBolze SGrouin JMJeannin Megnien SDubourg J, et al. (2021) Efficacy and safety of PXL770, a direct AMP kinase activator, for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (STAMP-NAFLD): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:889–902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

