Previous dry socket as a risk factor for alveolar osteitis: A nested case-control study in primary healthcare services
- PMID: 35765360
- PMCID: PMC9233910
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.59586
Previous dry socket as a risk factor for alveolar osteitis: A nested case-control study in primary healthcare services
Abstract
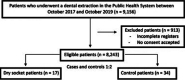
Background: Dry socket is one of the most common complications following tooth extraction, though no studies have been made on its main risk factors in the primary healthcare services of Barcelona (Spain). Objectives: To analyze the influence of different factors upon the appearance of dry socket in patients attended in the primary care setting, and to determine the possible presence of risk factors in patients who have suffered a previous episode of dry socket.
Material and methods: During 24 months, questionnaires were filled with data on the patients seen in different public primary healthcare services in the area of Barcelona (Spain). A case-control study was conducted to identify the main risk factors for developing complications in the form of dry socket.
Results: A mandibular location of the extracted tooth, poor oral hygiene, difficult extraction, and previous dry socket increased the risk of developing this complication. In patients with dry socket in the past, the risk of developing the same complication again, adjusted for difficulty of extraction, was seen to increase 11.45-fold (OR: 11.45; 95%CI: 1.06 to 123.74; p = 0.045).
Conclusions: The risk factors for dry socket are a mandibular location of the extracted tooth, poor oral hygiene, difficult extraction, and particularly a history of dry socket in the past. The identification of these factors the prevention of dry socket in each patient could be improved. Key words:Dry socket, risk factors, extraction, complications.
Copyright: © 2022 Medicina Oral S.L.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. There was no source of funding for this study, which was carried out by the “Dental and Maxillofacial Pathology and Therapeutics” research group of the IDIBELL Institute (Spain).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of immediate post-extraction socket irrigation on development of alveolar osteitis after mandibular third molar removal: a prospective split-mouth study, preliminary report.Br Dent J. 2012 Dec;213(12):597-601. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2012.1134. Br Dent J. 2012. PMID: 23257808
-
Common risk factors of dry socket (alveolitis osteitis) following dental extraction: A brief narrative review.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018 Nov;119(5):407-411. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2018.04.011. Epub 2018 Apr 30. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018. PMID: 29723658 Review.
-
Alveolar Osteitis: Patient's Compliance with Post-extraction Instructions Following Permanent Teeth Extraction.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018 Dec 1;19(12):1517-1524. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018. PMID: 30713183
-
Incidence and pattern of presentation of dry socket following non-surgical tooth extraction.Nig Q J Hosp Med. 2007 Oct-Dec;17(4):126-30. Nig Q J Hosp Med. 2007. PMID: 18320756
-
Surgical techniques for the removal of mandibular wisdom teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 26;7(7):CD004345. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004345.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32712962 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Frequency and etiological denominators of alveolar osteitis at Northern Province of Kingdom of Saudi Arabia-An observational study.SAGE Open Med. 2023 Dec 24;11:20503121231219420. doi: 10.1177/20503121231219420. eCollection 2023. SAGE Open Med. 2023. PMID: 38146494 Free PMC article.
-
Postextraction infections, prevention, and treatment.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Aug 1;42(4):426-434. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2024.2023427. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39049629 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Dry Socket Prevalence and Risk Factors in Third Molar Extractions: A Prospective Observational Study.Cureus. 2024 Mar 22;16(3):e56721. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56721. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38646199 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of Dry Socket with Ozone Oil-Based Gel after Inferior Third Molar Extraction: A Double-Blind Split-Mouth Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.Gels. 2023 Apr 1;9(4):289. doi: 10.3390/gels9040289. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37102901 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) in the Management of Dry Socket: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 19;25(18):10069. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810069. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burgoyne CC, Giglio JA, Reese SE, Sima AP, Laskin DM. The efficacy of a topical anesthetic gel in the relief of pain associated with localized alveolar osteitis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68:144–8. - PubMed
-
- Daly B, Sharif MO, Newton T, Jones K, Worthington H V. Local interventions for the management of alveolar osteitis (dry socket) Cochrane database Syst Rev. 2012;12:CD006968. - PubMed
-
- Blum IR. Contemporary views on dry socket (alveolar osteitis): A clinical appraisal of standardization, aetiopathogenesis and management: A critical review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;31:309–17. - PubMed
-
- Bienek DR, Filliben JJ. Risk assessment and sensitivity meta-analysis of alveolar osteitis occurrence in oral contraceptive users. J Am Dent Assoc. 2016;147:394–404. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous