Pattern and Visual Prognostic Factors of Behcet's Uveitis in Northwest Iran
- PMID: 35765637
- PMCID: PMC9185191
- DOI: 10.18502/jovr.v17i2.10796
Pattern and Visual Prognostic Factors of Behcet's Uveitis in Northwest Iran
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the pattern of ocular involvement in Behcet's disease (BD) with predictors of patients' final state of vision.
Methods: This historical cohort encompassed the clinical records of 200 patients diagnosed according to the International Criteria for BD (ICBD), over a period of 17 years between 2004 and 2021.
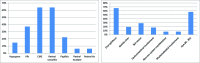
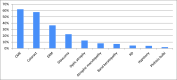
Results: The prevalence of Behcet's uveitis (BU) was more common in females and patients in the fourth decade of life. Ninety-five patients (47.5%) had evidence of ocular involvement in the initial ophthalmologic evaluation, and 171 patients (85.5%) manifested evidence of BU during the follow-up visits of which bilateral non-granulomatous panuveitis was the most common anatomical pattern of involvement (32.9%) followed by posterior (27.6%), anterior (26.5%), and intermediate (13.8%) uveitis. The prevalent accompanying signs were oral aphthous (67%), skin lesions (29%), and genital ulcers (19.5%). Cystoid macular edema (CME) was the most frequent ocular complication (62%), followed by cataract (57.5%) and epiretinal membranes (ERM) (36.5%). Univariate analysis showed the following determinants: male gender, younger age at onset, panuveitis, posterior uveitis, retinal vasculitis, and longer duration of uveitis as poorer visual prognostic factors of the disease. Multivariate analysis demonstrated a higher chance of poor visual prognosis of BD in patients with panuveitis, posterior uveitis, retinal vasculitis, and longer duration of uveitis.
Conclusion: This cohort study demonstrated an overview on epidemiological patterns of BU along with the visual prognostic factors in Iranian patients.
Keywords: Behcet's Syndrome; Behcet's Uveitis; Iran; Prognosis; Uveitis; Behcet's Disease.
Copyright © 2022 Ghavidel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Yazici H, Seyahi E, Hatemi G, Yazici Y. Behçet syndrome: a contemporary view. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14:107. - PubMed
-
- Khairallah M, Accorinti M, Muccioli C, Kahloun R, Kempen JH. Epidemiology of Behçet disease. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2012;20:324–335. - PubMed
-
- Horie Y, Meguro A, Ohta T, Lee EB, Namba K, Mizuuchi K, et al. HLA-B51 carriers are susceptible to ocular symptoms of Behçet disease and the association between the two becomes stronger towards the east along the silk road: a literature survey. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2017;25:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Meguro A, Inoko H, Ota M, Katsuyama Y, Oka A, Okada E, et al. Genetics of Behçet disease inside and outside the MHC. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:747–754. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
