Automated identification of chicken distress vocalizations using deep learning models
- PMID: 35765806
- PMCID: PMC9240672
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2021.0921
Automated identification of chicken distress vocalizations using deep learning models
Abstract
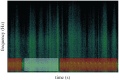
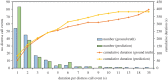
The annual global production of chickens exceeds 25 billion birds, which are often housed in very large groups, numbering thousands. Distress calling triggered by various sources of stress has been suggested as an 'iceberg indicator' of chicken welfare. However, to date, the identification of distress calls largely relies on manual annotation, which is very labour-intensive and time-consuming. Thus, a novel convolutional neural network-based model, light-VGG11, was developed to automatically identify chicken distress calls using recordings (3363 distress calls and 1973 natural barn sounds) collected on an intensive farm. The light-VGG11 was modified from VGG11 with significantly fewer parameters (9.3 million versus 128 million) and 55.88% faster detection speed while displaying comparable performance, i.e. precision (94.58%), recall (94.89%), F1-score (94.73%) and accuracy (95.07%), therefore more useful for model deployment in practice. To additionally improve light-VGG11's performance, we investigated the impacts of different data augmentation techniques (i.e. time masking, frequency masking, mixed spectrograms of the same class and Gaussian noise) and found that they could improve distress calls detection by up to 1.52%. Our distress call detection demonstration on continuous audio recordings, shows the potential for developing technologies to monitor the output of this call type in large, commercial chicken flocks.
Keywords: animal welfare; bioacoustics; convolutional neural networks; data augmentation; precision livestock farming.
Figures


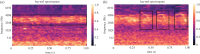


References
-
- Briefer EF, Tettamanti F, McElligott AG. 2015. Emotions in goats: mapping physiological, behavioural and vocal profiles. Anim. Behav. 99, 131-143. (10.1016/j.anbehav.2014.11.002) - DOI
-
- McGrath N, Dunlop R, Dwyer CD, Burman O, Phillips CJC. 2017. Hens vary their vocal repertoire and structure when anticipating different types of reward. Anim. Behav. 130, 79-96. (10.1016/j.anbehav.2017.05.025) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
