Novel Risk Prediction Model to Determine Adverse Heart Failure Outcomes in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 35766284
- PMCID: PMC9333366
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.121.024634
Novel Risk Prediction Model to Determine Adverse Heart Failure Outcomes in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
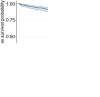
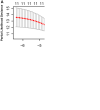
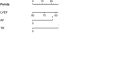
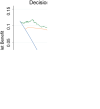
Background Patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy are at risk for life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias, but progressive heart failure (HF) may occur in later stages of disease. This study aimed to characterize potential risk predictors and develop a model for individualized assessment of adverse HF outcomes in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Methods and Results Longitudinal and observational cohorts with 290 patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy from the Fuwai Hospital in Beijing, China, and 99 patients from the University Heart Center in Zurich, Switzerland, with follow-up data were studied. The primary end point of the study was heart transplantation or death attributable to HF. The model was developed by Cox regression analysis for predicting risk and was internally validated. During 4.92±3.03 years of follow-up, 48 patients reached the primary end point. The determinants of the risk prediction model were left ventricular ejection fraction, serum creatinine levels, moderate-to-severe tricuspid regurgitation, and atrial fibrillation. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators did not reduce the occurrence of adverse HF outcomes. Conclusions A novel risk prediction model for arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy has been developed using 2 large and well-established cohorts, incorporating common clinical parameters such as left ventricular ejection fraction, serum creatinine levels, tricuspid regurgitation, and atrial fibrillation, which can identify patients who are at risk for terminal HF events, and may guide physicians to assess individualized HF risk and to optimize management strategies.
Keywords: arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy; heart failure; heart transplantation; outcome; risk prediction.
Figures


Comment in
-
Predicting Heart Failure in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Jul 5;11(13):e026874. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026874. Epub 2022 Jun 29. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35766273 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- DeWitt ES, Chandler SF, Hylind RJ, Beausejour Ladouceur V, Blume ED, VanderPluym C, Powell AJ, Fynn‐Thompson F, Roberts AE, Sanders SP, et al. Phenotypic manifestations of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy in children and adolescents. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:346–358. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.05.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bosman LP, Sammani A, James CA, Cadrin‐Tourigny J, Calkins H, van Tintelen JP, Hauer RNW, Asselbergs FW, Te Riele A. Predicting arrhythmic risk in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Heart Rhythm. 2018;15:1097–1107. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.01.031 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cadrin‐Tourigny J, Bosman LP, Nozza A, Wang W, Tadros R, Bhonsale A, Bourfiss M, Fortier A, Lie OH, Saguner AM, et al. A new prediction model for ventricular arrhythmias in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:1850–1858. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz103 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

