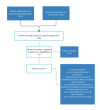
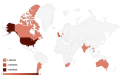
Learning impacts on elementary education students during physical and social distancing due COVID-19
- PMID: 35766749
- PMCID: PMC9886128
- DOI: 10.1590/2317-1782/20212020373
Learning impacts on elementary education students during physical and social distancing due COVID-19
Abstract
The social and physical isolation caused by COVID-19 changed the world's educational reality. This article aimed to identify publications in the world literature that report the impacts of such isolation on the learning process of children and adolescents in elementary education. The results showed that among the fourteen studies analyzed, there is an alert to the students in situations of social vulnerability, with the worse repercussions on girls at risk for early pregnancy and overload of domestic work, as well as academic losses due to the absence of food in the school context of those who depends on the school to survive. There are still few studies that give direction to students with educational special needs and, in Brazil, there are no studies correlating the learning process with elementary education students during the COVID-19 pandemic.
O isolamento físico social ocasionado pela pandemia do COVID-19 trouxe mudanças na realidade educacional mundial. O objetivo deste artigo foi identificar na literatura mundial artigos que relatam os impactos deste isolamento na aprendizagem de crianças e adolescentes da educação básica. Os resultados evidenciaram que, dentre os quatorze estudos analisados, há um alerta para os estudantes em situação de vulnerabilidade social, com pior repercussão em meninas em situação de risco para gestação precoce e sobrecarga de trabalho doméstico, assim como prejuízos acadêmicos em virtude da ausência da alimentação no contexto escolar daqueles que dependem da escola para sobrevivência. Ainda há poucos estudos que direcionam a atenção para estudantes com necessidades educacionais especiais e, no Brasil, não há estudos relacionados à aprendizagem com estudantes da educação básica durante a pandemia da COVID-19.
RESUMO: O isolamento físico social ocasionado pela pandemia do COVID-19 trouxe mudanças na realidade educacional mundial. O objetivo deste artigo foi identificar na literatura mundial artigos que relatam os impactos deste isolamento na aprendizagem de crianças e adolescentes da educação básica. Os resultados evidenciaram que, dentre os quatorze estudos analisados, há um alerta para os estudantes em situação de vulnerabilidade social, com pior repercussão em meninas em situação de risco para gestação precoce e sobrecarga de trabalho doméstico, assim como prejuízos acadêmicos em virtude da ausência da alimentação no contexto escolar daqueles que dependem da escola para sobrevivência. Ainda há poucos estudos que direcionam a atenção para estudantes com necessidades educacionais especiais e, no Brasil, não há estudos relacionados à aprendizagem com estudantes da educação básica durante a pandemia da COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: nothing to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Tabile AF, Jacometo MCD. Fatores influenciadores no processo de aprendizagem: um estudo de caso. Rev Psicopedagogia. 2017;34(103):75–86.
-
- WHO: World Health Organization . WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. Geneva: WHO; 2020. [citado em 2021 Fev 28]. Internet. Disponível em: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- UNESCO: United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization . School closures caused by Coronavirus (COVID-19) Paris: UNESCO; 2020. [citado em 2020 Out 28]. Internet. Disponível em: https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse .
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical