SARS-CoV-2 infection and liver involvement
- PMID: 35767172
- PMCID: PMC9243815
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-022-10364-1
SARS-CoV-2 infection and liver involvement
Abstract
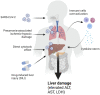
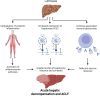
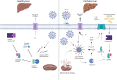
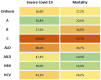
The COVID-19 pandemic is the largest public health challenge in living memory. Patients with underlying liver disease have been disproportionately affected, experiencing high morbidity and mortality. In addition, elevated liver enzymes appear to be a risk factor for disease progression, even in the absence of underlying liver disease. Nevertheless, the mechanism of liver injury in SARS-CoV-2 infection remains largely unknown. This review aims to provide an overview of the mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 induces liver injury, and the impact of COVID-19 on cirrhosis, alcohol-related liver disease, autoimmune liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatitis B and C virus infection, liver-transplant recipients and patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Finally, emerging data on vaccination in liver diseases is discussed, to help inform public health policy.
Keywords: Alcohol-related liver disease; Autoimmune liver disease; COVID-19; Chronic liver disease; Cirrhosis; Hepatitis B virus infection; Liver injury; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; SARS-CoV-2; Vaccination.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RJ has research collaborations with Takeda and Yaqrit, consults for Mallinckrodt and Yaqrit and has received speaking fees from Grifols. RJ is the founder of Yaqrit Limited and Thoeris GmBh, which is developing UCL inventions for treatment of patients with cirrhosis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

