Effects of image homogeneity on stenosis visualization at 7 T in a coronary artery phantom study: With and without B1-shimming and parallel transmission
- PMID: 35767553
- PMCID: PMC9242506
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270689
Effects of image homogeneity on stenosis visualization at 7 T in a coronary artery phantom study: With and without B1-shimming and parallel transmission
Abstract
Background: To investigate the effects of B1-shimming and radiofrequency (RF) parallel transmission (pTX) on the visualization and quantification of the degree of stenosis in a coronary artery phantom using 7 Tesla (7 T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods: Stenosis phantoms with different grades of stenosis (0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100%; 5 mm inner vessel diameter) were produced using 3D printing (clear resin). Phantoms were imaged with four different concentrations of diluted Gd-DOTA representing established arterial concentrations after intravenous injection in humans. Samples were centrally positioned in a thorax phantom of 30 cm diameter filled with a custom-made liquid featuring dielectric properties of muscle tissue. MRI was performed on a 7 T whole-body system. 2D-gradient-echo sequences were acquired with an 8-channel transmit 16-channel receive (8 Tx / 16 Rx) cardiac array prototype coil with and without pTX mode. Measurements were compared to those obtained with identical scan parameters using a commercially available 1 Tx / 16 Rx single transmit coil (sTX). To assess reproducibility, measurements (n = 15) were repeated at different horizontal angles with respect to the B0-field.
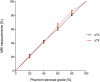
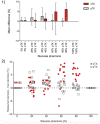
Results: B1-shimming and pTX markedly improved flip angle homogeneity across the thorax phantom yielding a distinctly increased signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) averaged over a whole slice relative to non-manipulated RF fields. Images without B1-shimming showed shading artifacts due to local B1+-field inhomogeneities, which hampered stenosis quantification in severe cases. In contrast, B1-shimming and pTX provided superior image homogeneity. Compared with a conventional sTX coil higher grade stenoses (60% and 80%) were graded significantly (p<0.01) more precise. Mild to moderate grade stenoses did not show significant differences. Overall, SNR was distinctly higher with B1-shimming and pTX than with the conventional sTX coil (inside the stenosis phantoms 14%, outside the phantoms 32%). Both full and half concentration (10.2 mM and 5.1 mM) of a conventional Gd-DOTA dose for humans were equally suitable for stenosis evaluation in this phantom study.
Conclusions: B1-shimming and pTX at 7 T can distinctly improve image homogeneity and therefore provide considerably more accurate MR image analysis, which is beneficial for imaging of small vessel structures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Task Force Members, Montalescot G, Sechtem U, Achenbach S, Andreotti F, Arden C, et al. 2013 ESC guidelines on the management of stable coronary artery disease: the Task Force on the management of stable coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology. European Heart Journal. 2013. pp. 2949–3003. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht296 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fihn SD, Gardin JM, Abrams J, Berra K, Blankenship JC, Dallas AP, et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA/ACP/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS guideline for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines, and the American College of Physicians, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. 11 ed. Circulation. 2012. pp. e354–471. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e318277d6a0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Zhao X, Huang J, Francois CJ, Tuite D, Bi X, et al. Comparison of 3D free-breathing coronary MR angiography and 64-MDCT angiography for detection of coronary stenosis in patients with high calcium scores. AJR Am J Roentgenol. American Roentgen Ray Society; 2007;189:1326–32. doi: 10.2214/AJR.07.2805 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

