Glucose level detection using millimetre-wave metamaterial-inspired resonator
- PMID: 35767587
- PMCID: PMC9242449
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269060
Glucose level detection using millimetre-wave metamaterial-inspired resonator
Abstract
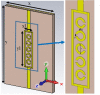
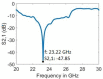
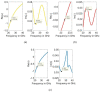
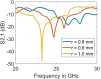
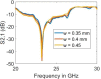
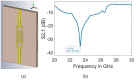
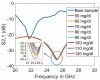
Millimetre-wave frequencies are promising for sensitive detection of glucose levels in the blood, where the temperature effect is insignificant. All these features provide the feasibility of continuous, portable, and accurate monitoring of glucose levels. This paper presents a metamaterial-inspired resonator comprising five split-rings to detect glucose levels at 24.9 GHz. The plexiglass case containing blood is modelled on the sensor's surface and the structure is simulated for the glucose levels in blood from 50 mg/dl to 120 mg/dl. The novelty of the sensor is demonstrated by the capability to sense the normal glucose levels at millimetre-wave frequencies. The dielectric characteristics of the blood are modelled by using the Debye parameters. The proposed design can detect small changes in the dielectric properties of blood caused by varying glucose levels. The variation in the transmission coefficient for each glucose level tested in this study is determined by the quality factor and resonant frequency. The sensor presented can detect the change in the quality factor of transmission response up to 2.71/mg/dl. The sensor's performance has also been tested to detect diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome. The sensor showed a linear shift in resonant frequency with the change in glucose levels, and an R2 of 0.9976 was obtained by applying regression analysis. Thus, the sensor can be used to monitor glucose in a normal range as well as at extreme levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures









References
-
- Williams R. Diabetes and the Disadvantaged and Vulnerable. US Endocrinol [Internet]. 2006;00(01):16. Available from: http://www.touchendocrinology.com/articles/diabetes-and-disadvantaged-an...
-
- Omer AE, Shaker G, Safavi-Naeini S. Non-invasive Glucose Monitoring at mm-Wave Frequencies. J Comput Vis Imaging Syst [Internet]. 2018. Dec 24;4(1):3. Available from: http://openjournals.uwaterloo.ca/index.php/vsl/article/view/325
-
- Turgul V, Kale I. On the accuracy of complex permittivity model of glucose/water solutions for non-invasive microwave blood glucose sensing. In: 2015 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB) [Internet]. IEEE; 2015. p. 1–4. Available from: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7391450/
-
- Villena Gonzales W, Mobashsher A, Abbosh A. The Progress of Glucose Monitoring—A Review of Invasive to Minimally and Non-Invasive Techniques, Devices and Sensors. Sensors [Internet]. 2019. Feb 15;19(4):800. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/19/4/800 doi: 10.3390/s19040800 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bilotti F, Sevgi L. Metamaterials: Definitions, properties, applications, and FDTD-based modeling and simulation (Invited paper). Int J RF Microw Comput Eng [Internet]. 2012. Jul;22(4):422–38. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/mmce.20634 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

