Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection in a paediatric cohort in Kuwait
- PMID: 35768102
- PMCID: PMC9240452
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-056371
Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection in a paediatric cohort in Kuwait
Abstract
Objective: Subsequent protection from SARS-CoV-2 infection in paediatrics is not well reported in the literature. We aimed to describe the clinical characteristics and dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 PCR repositivity in children.
Design: This is a population-level retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Patients were identified through multiple national-level electronic COVID-19 databases that cover all primary, secondary and tertiary centres in Kuwait.
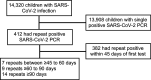
Participants: The study included children 12 years and younger between 28 February 2020 and 6 March 2021. SARS-CoV-2 reinfection was defined as having two or more positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR tests done on a respiratory sample, at least 45 days apart. Clinical data were obtained from the Pediatric COVID-19 Registry in Kuwait.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: The primary measure is to estimate SARS-CoV-2 PCR repositivity rate. The secondary objective was to establish average duration between first and subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection. Descriptive statistics were used to present clinical data for each infection episode. Also, incidence-sensitivity analysis was performed to evaluate 60-day and 90-day PCR repositivity intervals.
Results: Thirty paediatric patients with COVID-19 had SARS-CoV-2 reinfection at an incidence of 1.02 (95% CI 0.71 to 1.45) infection per 100 000 person-days and a median time to reinfection of 83 (IQR 62-128.75) days. The incidence of reinfection decreased to 0.78 (95% CI 0.52 to 1.17) and 0.47 (95% CI 0.28 to 0.79) per person-day when the minimum interval between PCR repositivity was increased to 60 and 90 days, respectively. The mean age of reinfected subjects was 8.5 (IQR 3.7-10.3) years and the majority (70%) were girls. Most children (55.2%) had asymptomatic reinfection. Fever was the most common presentation in symptomatic patients. One immunocompromised experienced two reinfection episodes.
Conclusion: SARS-CoV-2 reinfection is uncommon in children. Previous confirmed COVID-19 in children seems to result in a milder reinfection.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemiology; PAEDIATRICS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. World Health organization. World Health organization. Available: https://covid19.who.int/ [Accessed 1 May 2021].
-
- Children and COVID-19: State Data Report . American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association. Available: https://services.aap.org/en/pages/2019-novel-coronavirus-covid-19-infect... [Accessed 12 May 2021].
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous