Scoping review of costs of implementation strategies in community, public health and healthcare settings
- PMID: 35768106
- PMCID: PMC9240875
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-060785
Scoping review of costs of implementation strategies in community, public health and healthcare settings
Abstract
Objectives: To identify existing evidence concerning the cost of dissemination and implementation (D&I) strategies in community, public health and health service research, mapped with the 'Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change' (ERIC) taxonomy.
Design: Scoping review.
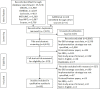
Data sources: MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, PsycINFO, Scopus and the Cochrane Library were searched to identify any English language reports that had been published between January 2008 and December 2019 concerning the cost of D&I strategies.
Data extraction: We matched the strategies identified in each article using ERIC taxonomies; further classified them into five areas (eg, dissemination, implementation, integration, capacity building and scale-up); and extracted the corresponding costs (total costs and cots per action target and per evidence-based programme (EBP) participant). We also recorded the reported level of costing methodology used for cost assessment of D&I strategies.
Results: Of the 6445 articles identified, 52 studies were eligible for data extraction. Lack of D&I strategy cost data was the predominant reason (55% of the excluded studies) for study exclusion. Predominant topic, setting, country and research design in the included studies were mental health (19%), primary care settings (44%), the US (35%) and observational (42%). Thirty-five (67%) studies used multicomponent D&I strategies (ranging from two to five discrete strategies). The most frequently applied strategies were Conduct ongoing training (50%) and Conduct educational meetings (23%). Adoption (42%) and reach (27%) were the two most frequently assessed outcomes. The overall costs of Conduct ongoing training ranged from $199 to $105 772 ($1-$13 973 per action target and $0.02-$412 per EBP participant); whereas the cost of Conduct educational meetings ranged from $987 to $1.1-$2.9 million/year ($33-$54 869 per action target and $0.2-$146 per EBP participant). The wide range of costs was due to the varying scales of the studies, intended audiences/diseases and the complexities of the strategy components. Most studies presented limited information on costing methodology, making interpretation difficult.
Conclusions: The quantity of published D&I strategy cost analyses is increasing, yet guidance on conducting and reporting of D&I strategy cost analysis is necessary to facilitate and promote the application of comparative economic evaluation in the field of D&I research.
Keywords: health economics; protocols & guidelines; public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
The Economic Impact of Smoking and of Reducing Smoking Prevalence: Review of Evidence.Tob Use Insights. 2015 Jul 14;8:1-35. doi: 10.4137/TUI.S15628. eCollection 2015. Tob Use Insights. 2015. PMID: 26242225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies to improve the implementation of workplace-based policies or practices targeting tobacco, alcohol, diet, physical activity and obesity.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 14;11(11):CD012439. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012439.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30480770 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural interventions for type 2 diabetes: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(21):1-45. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074526 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Estimating the potential value of MSM-focused evidence-based implementation interventions in three Ending the HIV Epidemic jurisdictions in the United States: a model-based analysis.J Int AIDS Soc. 2024 Jul;27 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):e26265. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26265. J Int AIDS Soc. 2024. PMID: 38965982 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and recommendations for collecting and quantifying implementation costs in practice: a qualitative interview study.Implement Sci Commun. 2024 Oct 11;5(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s43058-024-00648-y. Implement Sci Commun. 2024. PMID: 39394175 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare provider experiences of deploying a continuous remote patient monitoring pilot program during the COVID-19 pandemic: a structured qualitative analysis.Front Digit Health. 2023 Jun 28;5:1157643. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2023.1157643. eCollection 2023. Front Digit Health. 2023. PMID: 37483317 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation strategies to increase human papillomavirus vaccination uptake for adolescent girls in sub-Saharan Africa: A scoping review protocol.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 25;17(8):e0267617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267617. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36006961 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of experimentally tested implementation strategies across health and human service settings: evidence from 2010-2022.Implement Sci. 2024 Jun 24;19(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13012-024-01369-5. Implement Sci. 2024. PMID: 38915102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institutes of Health . Implementation science: about is. Available: https://cancercontrol.cancer.gov/IS/about.html [Accessed 19 Mar 2020].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical