Inactivation of the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway promotes melanoma
- PMID: 35768444
- PMCID: PMC9243107
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31399-w
Inactivation of the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway promotes melanoma
Abstract
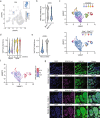
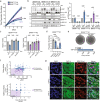
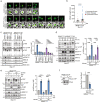
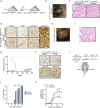
Melanoma is commonly driven by activating mutations in the MAP kinase BRAF; however, oncogenic BRAF alone is insufficient to promote melanomagenesis. Instead, its expression induces a transient proliferative burst that ultimately ceases with the development of benign nevi comprised of growth-arrested melanocytes. The tumor suppressive mechanisms that restrain nevus melanocyte proliferation remain poorly understood. Here we utilize cell and murine models to demonstrate that oncogenic BRAF leads to activation of the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway, both in melanocytes in vitro and nevus melanocytes in vivo. Mechanistically, we show that oncogenic BRAF promotes both ERK-dependent alterations in the actin cytoskeleton and whole-genome doubling events, which independently reduce RhoA activity to promote Hippo activation. We also demonstrate that functional impairment of the Hippo pathway enables oncogenic BRAF-expressing melanocytes to bypass nevus formation and rapidly form melanomas. Our data reveal that the Hippo pathway enforces the stable arrest of nevus melanocytes and represents a critical barrier to melanoma development.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- SEER*Explorer, National Program of Cancer Registries and Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results SEER*Stat Database: NPCR and SEER Incidence – U.S. Cancer Statistics Public Use Research Database, 2019 submission (2001–2017), United States Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Cancer Institute. www.cdc.gov/cancer/uscs/public-use (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

