The ventral midline thalamus coordinates prefrontal-hippocampal neural synchrony during vicarious trial and error
- PMID: 35768454
- PMCID: PMC9243057
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-14707-8
The ventral midline thalamus coordinates prefrontal-hippocampal neural synchrony during vicarious trial and error
Abstract
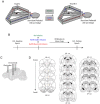
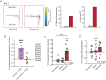
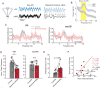
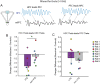
When faced with difficult choices, the possible outcomes are considered through a process known as deliberation. In rats, deliberation is thought to be reflected by pause-and-reorienting behaviors, better known as vicarious trial and errors (VTEs). While VTEs are thought to require medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and dorsal hippocampal (dHPC) interactions, no empirical evidence has yet demonstrated such a dual requirement. The nucleus reuniens (Re) of the ventral midline thalamus is anatomically connected with both the mPFC and dHPC, is required for HPC-dependent spatial memory tasks, and is critical for mPFC-dHPC neural synchronization. Currently, it is unclear if, or how, the Re is involved in deliberation. Therefore, by examining the role of the Re on VTE behaviors, we can better understand the anatomical and physiological mechanisms supporting deliberation. Here, we examined the impact of Re suppression on VTE behaviors and mPFC-dHPC theta synchrony during asymptotic performance of a HPC-dependent delayed alternation (DA) task. Pharmacological suppression of the Re increased VTE behaviors that occurred with repetitive choice errors. These errors were best characterized as perseverative behaviors, in which some rats repeatedly selected a goal arm that previously yielded no reward. We then examined the impact of Re suppression on mPFC-dHPC theta synchrony during VTEs. We found that during VTEs, Re inactivation was associated with a reduction in mPFC-dHPC theta coherence and mPFC-to-dHPC theta directionality. Our findings suggest that the Re contributes to deliberation by coordinating mPFC-dHPC neural interactions.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ventral Midline Thalamus Is Critical for Hippocampal-Prefrontal Synchrony and Spatial Working Memory.J Neurosci. 2016 Aug 10;36(32):8372-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0991-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27511010 Free PMC article.
-
Theta oscillations in the medial prefrontal cortex are modulated by spatial working memory and synchronize with the hippocampus through its ventral subregion.J Neurosci. 2013 Aug 28;33(35):14211-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2378-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23986255 Free PMC article.
-
Medial prefrontal and ventral hippocampal contributions to incidental context learning and memory in adolescent rats.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019 Dec;166:107091. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2019.107091. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019. PMID: 31542328
-
Role of the thalamic nucleus reuniens in mediating interactions between the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex during spatial working memory.Front Syst Neurosci. 2015 Mar 10;9:29. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2015.00029. eCollection 2015. Front Syst Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25805977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of the ventral midline thalamus in driving hippocampal functions.Prog Brain Res. 2015;219:145-61. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 May 16. Prog Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26072238 Review.
Cited by
-
[A study on the effects of learning on the properties of rats hippocampal-prefrontal connections in a memory task].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Dec 25;41(6):1095-1102. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202312042. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 40000197 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Flexible decision-making is related to strategy learning, vicarious trial and error, and medial prefrontal rhythms during spatial set-shifting.Learn Mem. 2024 Jul 22;31(7):a053911. doi: 10.1101/lm.053911.123. Print 2024 Jul. Learn Mem. 2024. PMID: 39038921 Free PMC article.
-
Theta-paced stimulation of the thalamic nucleus reuniens entrains mPFC-HPC oscillations and facilitates the acquisition of extinction memories.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 17:2025.08.15.670624. doi: 10.1101/2025.08.15.670624. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40832177 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Deliberative Behaviors and Prefrontal-Hippocampal Coupling are Disrupted in a Rat Model of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 29:2024.07.28.605480. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.28.605480. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 Mar 05;45(10):e1241242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1241-24.2025. PMID: 39131304 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Structural and functional organization of the midline and intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Aug 23;16:964644. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.964644. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36082310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muenzinger KF, Gentry E. Tone discrimination in white rats. J. Comp. Psychol. 1931;12:195–206. doi: 10.1037/h0072238. - DOI
-
- Muenzinger KF. Vicarious trial and error at a point of choice: I. A general survey of its relation to learning efficiency. Pedagog. Semin. J. Genet. Psychol. 1938;53(1):75–86.
-
- Tolman EC. Prediction of vicarious trial and error by means of the schematic sowbug. Psychol. Rev. 1939;46(4):318. doi: 10.1037/h0057054. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

