A method for AI assisted human interpretation of neonatal EEG
- PMID: 35768501
- PMCID: PMC9243143
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-14894-4
A method for AI assisted human interpretation of neonatal EEG
Abstract
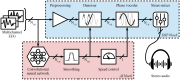
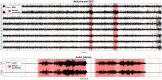
The study proposes a novel method to empower healthcare professionals to interact and leverage AI decision support in an intuitive manner using auditory senses. The method's suitability is assessed through acoustic detection of the presence of neonatal seizures in electroencephalography (EEG). Neurophysiologists use EEG recordings to identify seizures visually. However, neurophysiological expertise is expensive and not available 24/7, even in tertiary hospitals. Other neonatal and pediatric medical professionals (nurses, doctors, etc.) can make erroneous interpretations of highly complex EEG signals. While artificial intelligence (AI) has been widely used to provide objective decision support for EEG analysis, AI decisions are not always explainable. This work developed a solution to combine AI algorithms with a human-centric intuitive EEG interpretation method. Specifically, EEG is converted to sound using an AI-driven attention mechanism. The perceptual characteristics of seizure events can be heard using this method, and an hour of EEG can be analysed in five seconds. A survey that has been conducted among targeted end-users on a publicly available dataset has demonstrated that not only does it drastically reduce the burden of reviewing the EEG data, but also the obtained accuracy is on par with experienced neurophysiologists trained to interpret neonatal EEG. It is also shown that the proposed communion of a medical professional and AI outperforms AI alone by empowering the human with little or no experience to leverage AI attention mechanisms to enhance the perceptual characteristics of seizure events.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Newborns: Improving survival and well-being. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/newborns-reducing-morta... (2020).

