Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of epidural steroid injection using a nonparticulate steroid, dexamethasone or betamethasone: a double-blind, randomized, crossover, clinical trial
- PMID: 35768989
- PMCID: PMC9251387
- DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.3.336
Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of epidural steroid injection using a nonparticulate steroid, dexamethasone or betamethasone: a double-blind, randomized, crossover, clinical trial
Abstract
Background: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has prohibited epidural steroid injection (ESI) with particulate steroids. Thus, this study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of ESI with two nonparticulate steroids, dexamethasone and betamethasone.
Methods: The eligible patients (n = 600) who received ESI (0 week) with dexamethasone (ESI-dexa) or betamethasone (ESI-beta) had follow-up visits at 2, 4, and 8 weeks with a phone interview at 12 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of effective responders without pain or who were much improved at 2 weeks. The secondary endpoints were the proportion of crossover injections at 2 weeks; changes in the visual analog scale (VAS) and disability index scores at 2, 4, and 8 weeks; the number of additional ESIs in 12 weeks; the number of participants having spinal surgery, as well as the incidence of adverse events over the 12 weeks.
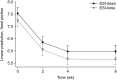
Results: The proportion of effective responders at 2 weeks was not different between ESI-beta (72/216, 33.3%) and ESI-dexa (63/200, 31.5%; P = 0.670). Adverse events were more common with ESI-dexa (40/200, 20.0%) than with ESI-beta (24/216, 11.1%; P = 0.012). VAS scores decreased more with ESI-beta than with ESI-dexa at 2 weeks (difference, 0.35; P = 0.023) and 4 weeks (difference, 0.42; P = 0.011). The disability score improved significantly more with ESI-beta compared with ESI-dexa at 2 weeks (difference, 3.37; P = 0.009), 4 weeks (difference, 4.01; P = 0.002), and 8 weeks (difference, 3.54; P = 0.007).
Conclusions: Betamethasone would be more appropriate for ESI.
Keywords: Betamethasone; Comparative Study; Dexamethasone; Epidural; Incidence; Injections; Pain; Spine; Steroids..
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial Comparing the Effectiveness of Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injections of Particulate and Nonparticulate Corticosteroids for Lumbosacral Radicular Pain.Pain Med. 2015 Sep;16(9):1697-708. doi: 10.1111/pme.12846. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Pain Med. 2015. PMID: 26095339 Clinical Trial.
-
Pain Reduction and Repeat Injections After Transforaminal Epidural Injection With Particulate Versus Nonparticulate Steroid for the Treatment of Chronic Painful Lumbosacral Radiculopathy.PM R. 2016 Nov;8(11):1039-1045. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2016.03.011. Epub 2016 Apr 6. PM R. 2016. PMID: 27060648
-
The noninferiority of the nonparticulate steroid dexamethasone vs the particulate steroids betamethasone and triamcinolone in lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections.Pain Med. 2013 Nov;14(11):1650-7. doi: 10.1111/pme.12214. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Pain Med. 2013. PMID: 23899304
-
Comparison of Particulate Steroid Injection vs Nonparticulate Steroid Injection for Lumbar Radicular Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2024 Sep;105(9):1756-1769. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2024.01.002. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38242297
-
Comparative effectiveness of lumbar epidural steroid injections using particulate vs. non-particulate steroid: an intra-individual comparative study.Skeletal Radiol. 2016 Feb;45(2):169-76. doi: 10.1007/s00256-015-2277-3. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Skeletal Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26537154
Cited by
-
Effects of dexamethasone combined with vitamin B12 on percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy early outcomes: a randomized controlled trial.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Nov 7;19(1):733. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05210-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39506779 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of analgesic effects between betamethasone and dexamethasone in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 9;12:1575417. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1575417. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40703273 Free PMC article.
-
An update on technical and safety practice patterns of interlaminar epidural steroid injections.Interv Pain Med. 2023 Nov 29;2(4):100371. doi: 10.1016/j.inpm.2023.100371. eCollection 2023 Dec. Interv Pain Med. 2023. PMID: 39239216 Free PMC article.
-
Data sharing: a direction for securing research transparency.Korean J Pain. 2022 Oct 1;35(4):359-360. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.4.359. Korean J Pain. 2022. PMID: 36175335 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Interaction between Dexamethasone, Ropivacaine, and Contrast Media Used in Interventional Pain Treatment: Considerations in Safety.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Dec 19;58(12):1871. doi: 10.3390/medicina58121871. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36557073 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

