Hepatoprotective Effect of Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidant Mito-TEMPO against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Injury in Mouse
- PMID: 35769207
- PMCID: PMC9236847
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6394199
Hepatoprotective Effect of Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidant Mito-TEMPO against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Injury in Mouse
Abstract
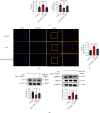
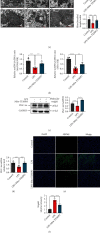
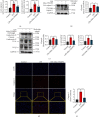
The liver is vulnerable to sepsis, and sepsis-induced liver injury is closely associated with poor survival of sepsis patients. Studies have found that the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is the major cause of oxidative stress, which is the main pathogenic factor for the progression of septic liver injury. The mitochondria are a major source of ROS. Mito-TEMPO is a mitochondria-specific superoxide scavenger. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of Mito-TEMPO on lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) induced sepsis mice. We found that Mito-TEMPO pretreatment inhibited inflammation, attenuated LPS-induced liver injury, and enhanced the antioxidative capability in septic mice, as evidenced by the decreased MDA content and the increased SOD activity. In addition, Mito-TEMPO restored mitochondrial size and improved mitochondrial function. Finally, we found that the levels of pyroptosis-related proteins in the liver of LPS-treated mice were lower after pretreatment with Mito-TEMPO. The mechanisms could be related to Mito-TEMPO enhanced antioxidative capability and improved mitochondrial function, which reflects the ability to neutralize ROS.
Copyright © 2022 Peng-Fei Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no known conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

