CD96 Downregulation Promotes the Immune Response of CD4 T Cells and Associates with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- PMID: 35769669
- PMCID: PMC9234051
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3946754
CD96 Downregulation Promotes the Immune Response of CD4 T Cells and Associates with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Abstract
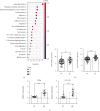
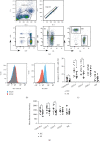
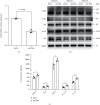
Inhibitory receptors (IRs) play an indispensable role in regulating T cell activation and expansion. This study is aimed at exploring the correlation between IRs and ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Bioinformatics analysis of two datasets (GSE25101 and GSE73754), including 68 AS cases and 36 healthy controls, demonstrated that "T cell receptor signaling pathway" was significantly enriched, and two IRs (CD112R and CD96) were downregulated in AS cases. Real-time Quantitative PCR Detecting System (qPCR) analysis confirmed the decreased expression of CD112R and CD96 in the peripheral blood of AS patients. Flow cytometry demonstrated that the frequency of CD96-positive cells among CD4 T cells in AS patients was significantly reduced and that expressed on the cells was also significantly lower than the healthy controls. In addition, the expression of CD96 was altered on human primary CD4 T cells extracted from 3 healthy volunteers and cocultured with allogeneic dendritic cells (DCs). Also, low expression of CD96 elevated the phosphorylation of ERK in CD4 T cells and increased the level of TNF-α, IL-23, IL-17A, IL-6, and IFN-γ in the cell culture supernatant. These results suggested that CD96 is crucial for the pathogenesis of AS and may be a potential target in the treatment of the disease.
Copyright © 2022 Fengqing Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of the nonspecific and antigen-specific T cell cytokine response in ankylosing spondylitis during treatment with infliximab.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Mar;48(3):780-90. doi: 10.1002/art.10847. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 12632433
-
Differential expression of CD96 surface molecule represents CD8⁺ T cells with dissimilar effector function during HIV-1 infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051696. Epub 2012 Dec 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23272144 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular cytokine patterns in Behçet's disease in comparison to ankylosing spondylitis--influence of treatment with interferon-alpha2a.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007 Jul-Aug;25(4 Suppl 45):S52-7. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17949552
-
TIGIT and CD96: new checkpoint receptor targets for cancer immunotherapy.Immunol Rev. 2017 Mar;276(1):112-120. doi: 10.1111/imr.12518. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28258695 Review.
-
Coming of Age: CD96 Emerges as Modulator of Immune Responses.Front Immunol. 2018 May 17;9:1072. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01072. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29868026 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nectin Family Ligands Trigger Immune Effector Functions in Health and Autoimmunity.Biology (Basel). 2023 Mar 15;12(3):452. doi: 10.3390/biology12030452. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Important Role in Novel Immune Mechanism and Diagnostic Model of Ankylosing Spondylitis: The CeRNA-ADRB2 Network.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Dec 6;16:5915-5936. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S431603. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 38084105 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

