From End to End: Gaining, Sorting, and Employing High-Density Neural Single Unit Recordings
- PMID: 35769832
- PMCID: PMC9236662
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2022.851024
From End to End: Gaining, Sorting, and Employing High-Density Neural Single Unit Recordings
Abstract
The meaning behind neural single unit activity has constantly been a challenge, so it will persist in the foreseeable future. As one of the most sourced strategies, detecting neural activity in high-resolution neural sensor recordings and then attributing them to their corresponding source neurons correctly, namely the process of spike sorting, has been prevailing so far. Support from ever-improving recording techniques and sophisticated algorithms for extracting worthwhile information and abundance in clustering procedures turned spike sorting into an indispensable tool in electrophysiological analysis. This review attempts to illustrate that in all stages of spike sorting algorithms, the past 5 years innovations' brought about concepts, results, and questions worth sharing with even the non-expert user community. By thoroughly inspecting latest innovations in the field of neural sensors, recording procedures, and various spike sorting strategies, a skeletonization of relevant knowledge lays here, with an initiative to get one step closer to the original objective: deciphering and building in the sense of neural transcript.
Keywords: algorithm evaluation; clustering; neural sensors; single unit recordings; spike sorting.
Copyright © 2022 Bod, Rokai, Meszéna, Fiáth, Ulbert and Márton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
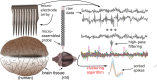
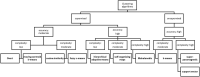
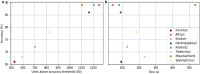
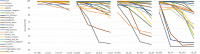

Similar articles
-
Spike sorting algorithms and their efficient hardware implementation: a comprehensive survey.J Neural Eng. 2023 Apr 14;20(2). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/acc7cc. J Neural Eng. 2023. PMID: 36972585 Review.
-
Towards online spike sorting for high-density neural probes using discriminative template matching with suppression of interfering spikes.J Neural Eng. 2018 Oct;15(5):056005. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aace8a. Epub 2018 Jun 22. J Neural Eng. 2018. PMID: 29932426
-
A robust spike sorting method based on the joint optimization of linear discrimination analysis and density peaks.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 15;12(1):15504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19771-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36109581 Free PMC article.
-
SpikeDeep-classifier: a deep-learning based fully automatic offline spike sorting algorithm.J Neural Eng. 2021 Feb 5;18(1). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abc8d4. J Neural Eng. 2021. PMID: 33166944
-
A review on cluster estimation methods and their application to neural spike data.J Neural Eng. 2018 Jun;15(3):031003. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aab385. Epub 2018 Mar 2. J Neural Eng. 2018. PMID: 29498353 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional clustering of neuronal signals with FMM mixture models.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 10;9(10):e20639. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20639. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37867904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmadi N., Constandinou T. G., Bouganis C.-S. (2020). Improved spike-based brain-machine interface using bayesian adaptive kernel smoother and deep learning. techRxiv. 10, 29341–29356. 10.36227/techrxiv.12383600.v1 - DOI
-
- Ahmadpour S., Behrad A., Vega I. F. (2019). Dark neurons: a protective mechanism or a mode of death. J. Med. Histol. 3, 125–131. 10.21608/jmh.2020.40221.1081 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

