Alteration of Peripheral Resistin and the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35770007
- PMCID: PMC9234264
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.915152
Alteration of Peripheral Resistin and the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Resistin is a small secretory adipokine which is implicated to obesity and associated diseases. Recently, plenty of research papers have been conducted to explore the association between peripheral resistin and the severity of acute pancreatitis (AP). However, the results were controversial. In this study, we aimed to confirm the effect of peripheral resistin and the development of acute pancreatitis.
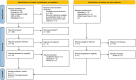
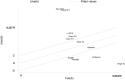
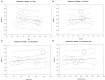
Methods: A comprehensive online search was performed using the PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CNKI, and Wanfang databases up through January 20, 2022. The retrieved records and their references were screened to identify additional studies. Data were extracted to calculate the pooled Hedges' g and its 95% CI, which were selected to assess peripheral resistin levels and the severity of acute pancreatitis. Subgroup analyses, sensitivity analyses, meta-regression, and publication bias tests were also undertaken based on obtained information.
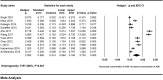
Results: A total of eleven studies with 892 acute pancreatitis patients were enrolled in the study. Peripheral resistin levels were significantly increased in severe acute pancreatitis compared with mild acute pancreatitis (Hedges' g = 2.092, 95% CI: 0.994-3.190, P < 0.001). Subgroup analyses based on sample types and ethnicity also showed similar results. A single study did not affect our results, which was verified by sensitivity analysis. Meta-regression analyses revealed that age, gender of the included subjects, sample size, and publication year did not moderate effects on the present results.
Conclusion: In our study, peripheral resistin levels were significantly elevated in patients with severe AP compared with patients with mild AP. Abnormal resistin levels may provide us some new insights in predicting the severity of AP.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; association; plasma; resistin; serum.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Liu, Wang, Gan, Chen, Tao and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Predictive value of adipokines for the severity of acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan 13;24(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03126-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38218787 Free PMC article.
-
Resistin is not an appropriate biochemical marker to predict severity of acute pancreatitis: a case-controlled study.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 7;20(41):15351-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15351. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25386084 Free PMC article.
-
Value of adipokines in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis: comprehensive review.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Dec 7;18(45):6620-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6620. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23236237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between peripheral blood levels of C-reactive protein and Autism Spectrum Disorder in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Aug;88:432-441. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.008. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Brain Behav Immun. 2020. PMID: 32272227
-
Can serum resistin predict severity of acute pancreatitis?Biomarkers. 2021 Feb;26(1):31-37. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2020.1841295. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 33089708
Cited by
-
Anti-Obesity Effect of Chitoglucan in High-Fat-Induced Obesity Mice.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 24;20(1):281. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010281. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612600 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of adipokines for the severity of acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan 13;24(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03126-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38218787 Free PMC article.
-
New Synthesized Activating Transcription Factor 3 Inducer SW20.1 Suppresses Resistin-Induced Metabolic Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2023 May 23;11(6):1509. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061509. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371606 Free PMC article.
-
Acute pancreatitis: pathogenesis and emerging therapies.J Pancreatol. 2024 Mar;7(1):10-20. doi: 10.1097/JP9.0000000000000168. Epub 2024 Jan 2. J Pancreatol. 2024. PMID: 38524855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune markers of severe acute pancreatitis.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 1;40(5):389-395. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000001053. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38967941 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

