Risk of Autoimmune Diseases Following Optic Neuritis: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- PMID: 35770018
- PMCID: PMC9234206
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.903608
Risk of Autoimmune Diseases Following Optic Neuritis: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
Objectives: Optic neuritis is (ON) is believed to be an immune-mediated disease; however, the association between optic neuritis and autoimmune diseases remains unclear. This study aimed to identify the incidence rate and adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) of autoimmune diseases in patients with optic neuritis.
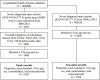
Methods: This nationwide, population-based, retrospective cohort study collected patients' data between 1999 and 2013 from the National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan. A total of 9,235 patients were included. Using 1:4 propensity scoring, 1,847 patients were enrolled in the optic neuritis group and 7,388 in the non-optic neuritis group according to age, sex, comorbidities, and corticosteroid use. Follow-up was started from the index date and the endpoint was a diagnosis of new-onset autoimmune diseases including, myasthenia gravis (MG), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
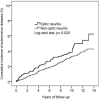
Results: The Kaplan-Meier curves depicted that patients with optic neuritis had a higher cumulative incidence of autoimmune diseases than patients without optic neuritis. Cox proportional hazard regression showed that patients with optic neuritis were at a high risk of autoimmune diseases (aHR: 1.40; 95% C.I., 1.05-1.87), including MG (aHR: 4.16, 95% C.I.: 1.33-12.94), SLE (aHR: 3.33, 95% C.I.: 1.24-8.97), and AS (aHR: 2.86, 95% C.I.: 1.54-5.31). Subgroup analysis provided that patients with optic neuritis aged below 65 years (aHR: 1.42, 95% C.I.: 1.03-1.96) or who were females (aHR: 1.59, 95% C.I.: 1.11-2.27) had a significantly increased risk of autoimmune diseases compared to respective controls. The use of corticosteroids reduced the risk of autoimmune diseases in patients with optic neuritis (aHR for corticosteroids non-users: 1.46, 95% C.I.: 1.03-2.07).
Conclusion: Patients with optic neuritis presented with a high risk of autoimmune diseases such as MG, SLE, and AS, especially patients with optic neuritis who were young or females. Corticosteroids attenuated the link between optic neuritis and subsequent autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis; autoimmune diseases; cohort study; myasthenia gravis; optic neuritis; psoriatic arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2022 Ma, Lee, Chen, Yang, Dong, Wang, Wei and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk of incident autoimmune diseases in patients with thymectomy.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020 Jul;7(7):1072-1082. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51055. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32478484 Free PMC article.
-
Proton Pump Inhibitors Increase the Risk of Autoimmune Diseases: A Nationwide Cohort Study.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 30;12:736036. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.736036. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34659225 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica after optic neuritis: A nationwide cohort study in Taiwan.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2020 Sep;44:102379. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2020.102379. Epub 2020 Jul 5. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2020. PMID: 32650124
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus-associated optic neuritis: clinical experience and literature review.Acta Ophthalmol. 2009 Mar;87(2):204-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2008.01193.x. Epub 2008 May 27. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 18507726 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in autoimmunity.Inflammopharmacology. 2020 Feb;28(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007/s10787-019-00651-z. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Inflammopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 31617124 Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of histone deacetylases in ocular diseases.Arch Pharm Res. 2024 Jan;47(1):20-39. doi: 10.1007/s12272-023-01482-x. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Arch Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38151648 Review.
-
Risk of primary Sjogren's Syndrome following human papillomavirus infections: a nationwide population-based cohort study.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 16;13:967040. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.967040. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36052092 Free PMC article.
-
Human Papillomavirus Infections and Increased Risk of Incident Osteoporosis: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study.Viruses. 2023 Apr 21;15(4):1021. doi: 10.3390/v15041021. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37113002 Free PMC article.
-
Ankylosing spondylitis and glaucoma in European population: A Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 20;14:1120742. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1120742. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37020551 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional support for successful weaning in patients undergoing prolonged mechanical ventilation.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 14;12(1):12044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15917-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35835785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davidson A, Diamond B. Autoimmune diseases. N Engl J Med. (2001) 345:340–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous