Oral SARS-CoV-2 Inoculation Causes Nasal Viral Infection Leading to Olfactory Bulb Infection: An Experimental Study
- PMID: 35770069
- PMCID: PMC9234459
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.924725
Oral SARS-CoV-2 Inoculation Causes Nasal Viral Infection Leading to Olfactory Bulb Infection: An Experimental Study
Abstract
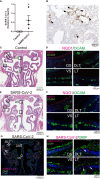
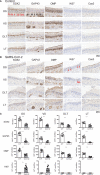
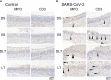
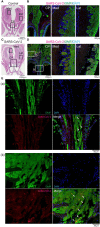
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections can cause long-lasting anosmia, but the impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection, which can spread to the nasal cavity via the oral route, on the olfactory receptor neuron (ORN) lineage and olfactory bulb (OB) remains undetermined. Using Syrian hamsters, we explored whether oral SARS-CoV-2 inoculation can lead to nasal viral infection, examined how SARS-CoV-2 affects the ORN lineage by site, and investigated whether SARS-CoV-2 infection can spread to the OB and induce inflammation. On post-inoculation day 7, SARS-CoV-2 presence was confirmed in the lateral area (OCAM-positive) but not the nasal septum of NQO1-positive and OCAM-positive areas. The virus was observed partially infiltrating the olfactory epithelium, and ORN progenitor cells, immature ORNs, and mature ORNs were fewer than in controls. The virus was found in the olfactory nerve bundles to the OB, suggesting the nasal cavity as a route for SARS-CoV-2 brain infection. We demonstrated that transoral SARS-CoV-2 infection can spread from the nasal cavity to the central nervous system and the possibility of central olfactory dysfunction due to SARS-CoV-2 infection. The virus was localized at the infection site and could damage all ORN-lineage cells.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; olfactory bulb; olfactory dysfunction; olfactory epithelium; oral inoculation; zone.
Copyright © 2022 Ueha, Ito, Furukawa, Kitabatake, Ouji-Sageshima, Ueha, Koyama, Uranaka, Kondo and Yamasoba.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brann D. H., Tsukahara T., Weinreb C., Lipovsek M., Van den Berge K., Gong B., et al. (2020). Non-Neuronal Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Genes in the Olfactory System Suggests Mechanisms Underlying COVID-19-Associated Anosmia. Sci. Adv. 6 (31), eabc5801. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc5801 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bryche B., St Albin A., Murri S., Lacote S., Pulido C., Ar Gouilh M., et al. (2020). Massive Transient Damage of the Olfactory Epithelium Associated With Infection of Sustentacular Cells by SARS-CoV-2 in Golden Syrian Hamsters. Brain Behav. Immun. 89, 579–586. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.06.032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

